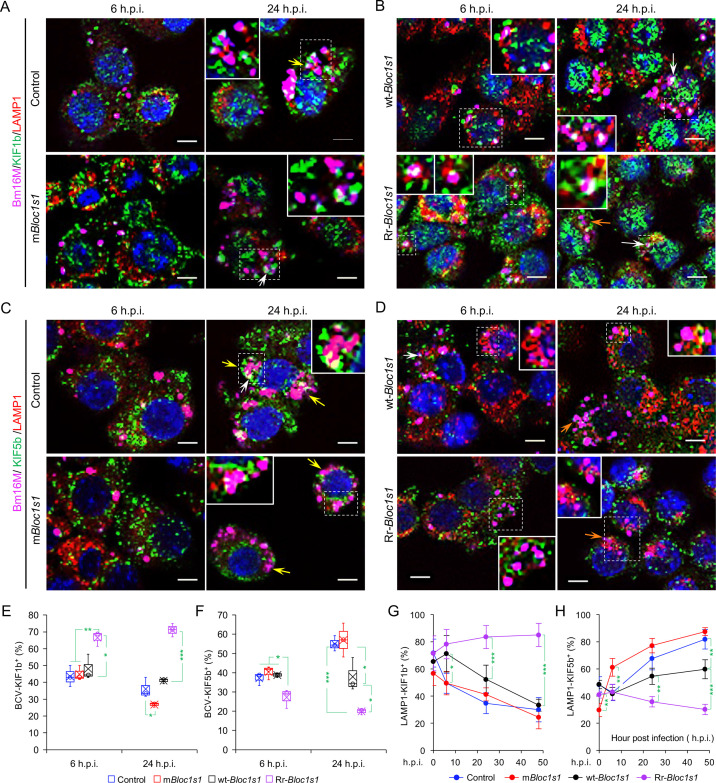
Figure 6. Brucella infection dissociates BORC-related lysosome trafficking factor KIF1b but recruits KIF5b.
Colocalization of KIF1b with BCVs or LAMP1 in the infected control and mBloc1s1 (A), or in wt-Bloc1s1 and Rr-Bloc1s1 (B) cells at the indicated h.p.i. Colocalization of KIF5b with BCVs or LAMP1 in the infected control and mBloc1s1 (C), or in wt-Bloc1s1 and Rr-Bloc1s1 (D) cells at the indicated h.p.i. White arrows: colocalization of BCVs with the indicated proteins. Insets: magnification of the selected areas (within windows with dash white lines). Yellow and orange arrows: the perinuclear and peripheral accumulation of BCVs-Lamp1, respectively. Bar: 5 μm. Quantification of BCV-KIF1b+ (E) and BCV-KIF5b+ (F) in Bm16M-infected cells at the indicated h.p.i. showing in A, B and C, D, respectively. Dynamics of LAMP1-KIF1b+ (G) or LAMP1-KIF5b+ (H) in a time course (48 hr) of Bm16M infection at the indicated h.p.i. Host cells were infected with or without Bm16M, and at the indicated h.p.i., the cells were fixed and subjected to confocal immunofluorescence assays. Images are representative of three independent experiments. Statistical data represent means ± standard error of mean (SEM) from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.