FIGURE 10.
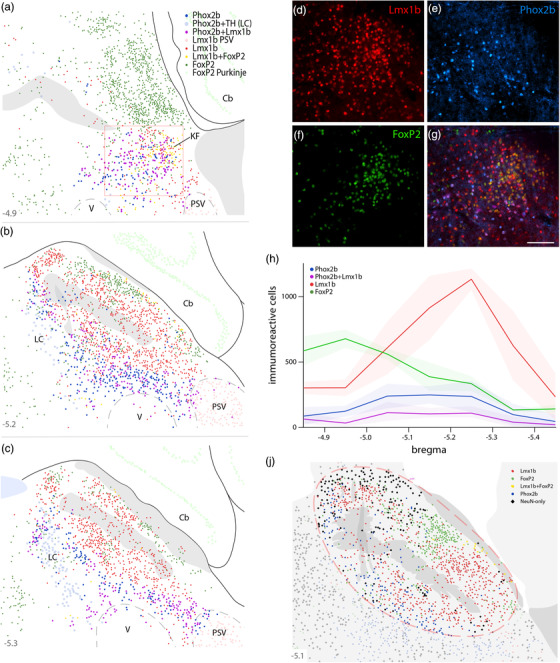
Labeling Phox2b, along with Lmx1b and FoxP2, identifies diverse populations of adult neurons in and around the PB. Neurons containing Phox2b alone (blue), Phox2b+Lmx1b (magenta), Lmx1b alone (red), Lmx1b+FoxP2 (yellow), or FoxP2 alone (green) were plotted at three rostral‐to‐caudal levels of the mouse PB (a–c). Approximate level caudal to bregma is shown at the bottom‐left of each panel (in mm). Phox2b‐containing neurons in the LC (TH+Phox2b) were plotted in light blue. FoxP2‐containing Purkinje neurons in the cerebellum were plotted in light green. Large, Lmx1b‐containing neurons in the principal sensory trigeminal nucleus (PSV) were plotted in light red. Ventral to the rostral PB (box in a), immunofluorescence labeling for Lmx1b (d, red), Phox2b (e, blue), FoxP2 (f, green), and all three combined (g) revealed focally diverse populations in the KF region. Scale bar in (g) is 50 μm. (h) Rostral‐to‐caudal counts of PB neurons containing Phox2b alone, Lmx1b alone, FoxP2 alone, or Phox2b+Lmx1b were averaged at each level (n = 3 mice), with variance represented by a standard deviation envelope; approximate levels caudal to bregma are labeled on the x‐axis. (i) Plotting the distribution of neurons containing only NeuN (black diamonds), without Phox2b, Lmx1b, or FoxP2, highlighted a remaining set of unidentified PB neurons. Approximate bregma level is shown at the bottom‐left of each panel (in mm)
