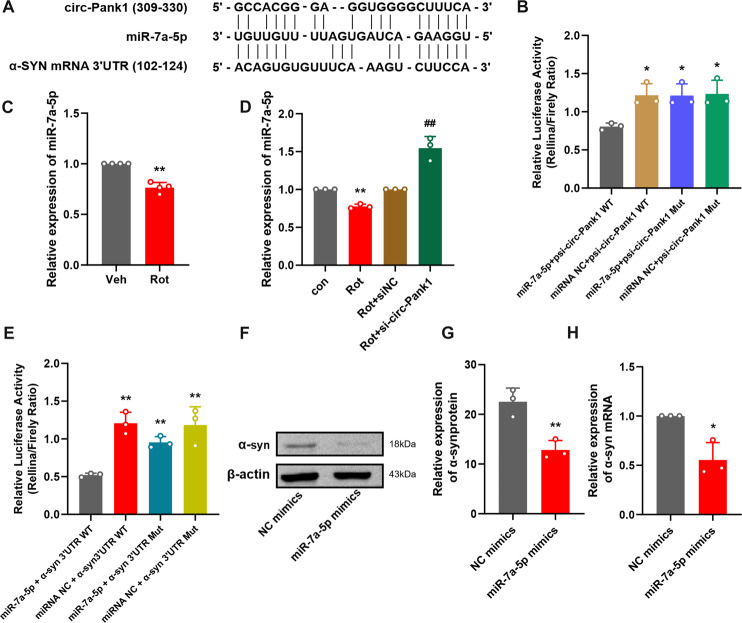
Fig. 4. Interaction between circ-Pank1/miR-7a-5p/a-syn in MN9D cells.
A Schematic diagram of binding sites between circ-Pank1 and the α-syn mRNA 3’UTR and miR-7a-5p. B The regulatory effect of circ-Pank1 on the expression of miR-7a-5p was verified by dual-luciferase reporter gene detection. The psi-circ-Pank-WT/Mut plasmid and miR-7a-5p mimic were cotransfected into HEK293T cells, and the luciferase activity was measured after 24 h (n = 3). C qRT–PCR was used to detect the expression of miR-7a-5p in the SN of PD model mice treated with rotenone (n = 4). D After si-circ-Pank1 and the corresponding control were transferred to the MN9D cell model treated with rotenone, the expression changes of miR-7a-5p were detected by qRT–PCR (n = 3). E The regulatory effect of miR-7a-5p on α-syn expression was verified by the dual-luciferase reporter gene detection. The psi-α-syn WT/Mut plasmid and miR-7a-5p mimic were co-transfected into HEK293T cells. After 24 h, the luciferase activity was measured. F–H After the transfection of miR-7a-5p mimics in MN9D cells (n = 3), Western blot analysis of α-syn protein levels F, G qRT–PCR detection of α-syn mRNA expression H. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.