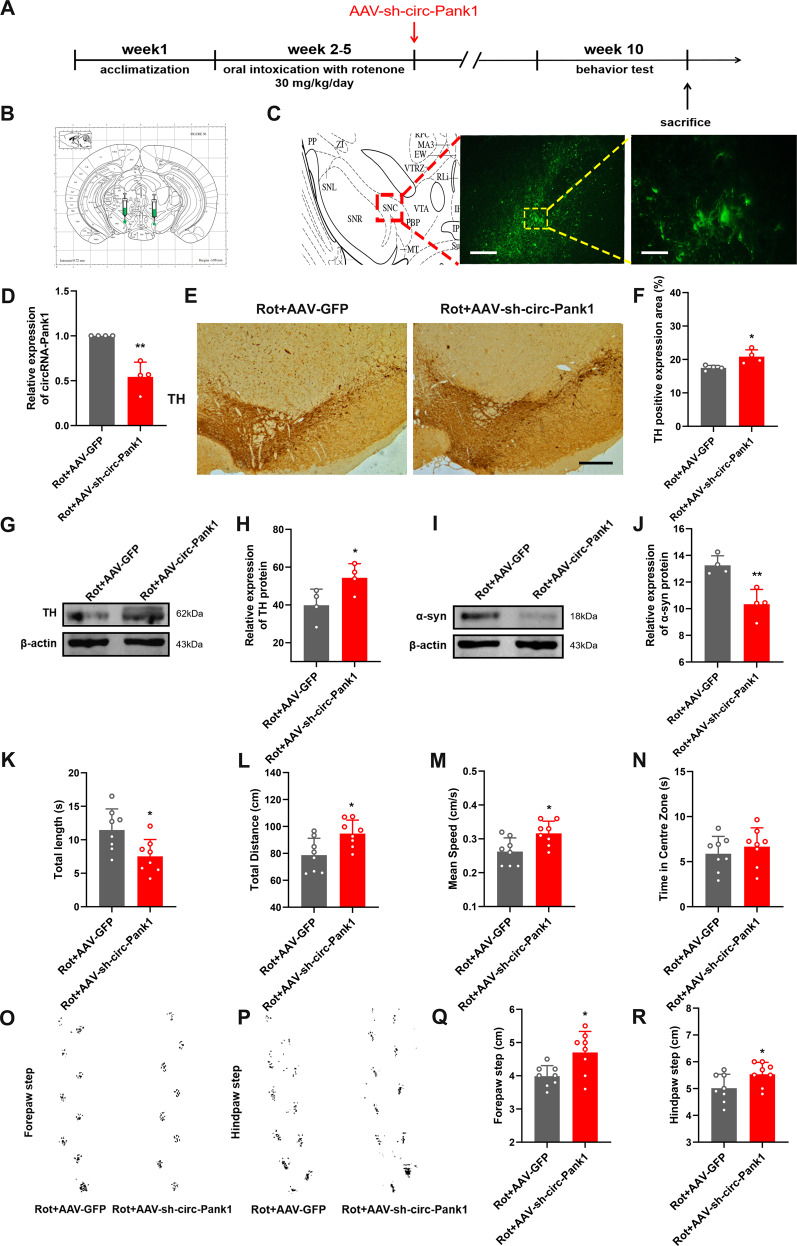
Fig. 6. Silencing circ-Pank1 can improve the PD-like motor dysfunction in mice treated with rotenone.
A Experimental schematic diagram. After 4 weeks of continuous administration of rotenone, the adeno-associated virus vector (AAV-sh-circ-Pank1) with fluorescence-specific knockdown of circ-Pank1 (AAV-sh-circ-Pank1) and the control GFP were injected by stereotactic brain injection. Adeno-associated virus vector (AAV-GFP) was injected into the SN of PD model mice treated with rotenone. B Schematic diagram of the brain stereotactic injection site of virus. C Representative fluorescence image of the virus-transfected section; scale bars, 100 μm and 50 μm. D qRT–PCR was used to detect the expression of circ-Pank1 after injection of AAV-sh-circ-Pank1 into the SN of PD model mice treated with rotenone (n = 4). E, F Immunohistochemical detection of the number of TH-positive cells after the injection of AAV-sh-circ-Pank1 into PD model mice treated with rotenone; scale bars, 500 μm (n = 4). G, H Western blot analysis of α-syn protein levels in the SN of PD model mice treated with rotenone after injection of AAV-sh-circ-Pank1. I, J Western blot analysis of TH protein levels in the SN of PD model mice treated with rotenone after the injection of AAV-sh-circ-Pank1 (n = 4). K–R PD model mice treated with rotenone after the injection of AAV-sh-circ-Pank1 were subjected to a pole climbing test K, field test (L–N) and step measurement (O–R) to evaluate the exercise ability (n = 8). Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.