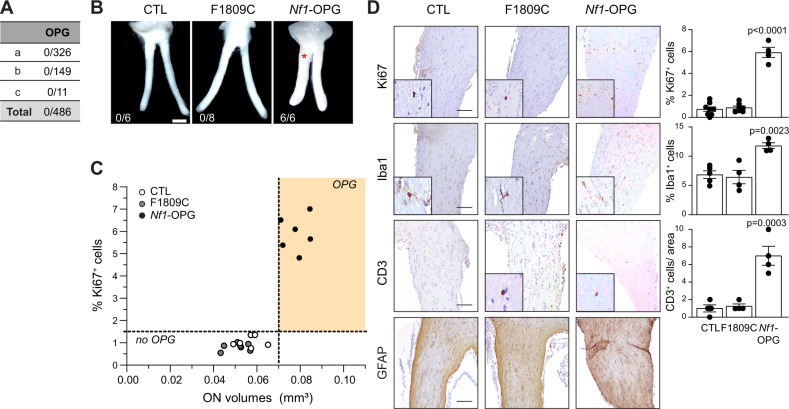
Fig. 1. Arg1809Cys Nf1-mutant mice do not develop optic gliomas following somatic Nf1 inactivation.
A Incidence of optic pathway glioma (OPG) in NF1 patients harboring the c.5425C > T NF1 germline mutation. (a)44, (b)45, (c)40. B Representative images of dissected optic nerves from control (Nf1f/f; CTL) and Nf1-mutant mice harboring conditional somatic Nf1 inactivation in neuroglial progenitors (Nf1f/1809; GFAP-Cre, F1809C; Nf1f/neo; GFAP-Cre, Nf1-OPG). Whereas Nf1-OPG mice form OPGs (red asterisk), CTL and F1809C mice do not. The number of mice that formed OPGs is shown in each panel. Scale bar: 1 mm. C Graph demonstrating the relationship between optic nerve volumes and Ki67+ cells in CTL, F1809C, and Nf1-OPG optic nerves. n = 6 for all groups. D Ki67, Iba1, CD3, and GFAP immunostaining of optic nerves in CTL, F1809C, and Nf1-OPG mice. Scale bars, 50 µm. (Ki67: CTL n = 8, F1809C n = 7, Nf1-OPG n = 4, P < 0.0001; Iba1: CTL n = 5, F1809C n = 4, Nf1-OPG n = 4, P = 0.0023; CD3: CTL n = 4, F1809C n = 4, Nf1-OPG n = 4, P = 0.0003). Data are represented as means ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test correction. P values are indicated within each panel. ns, not significant. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.