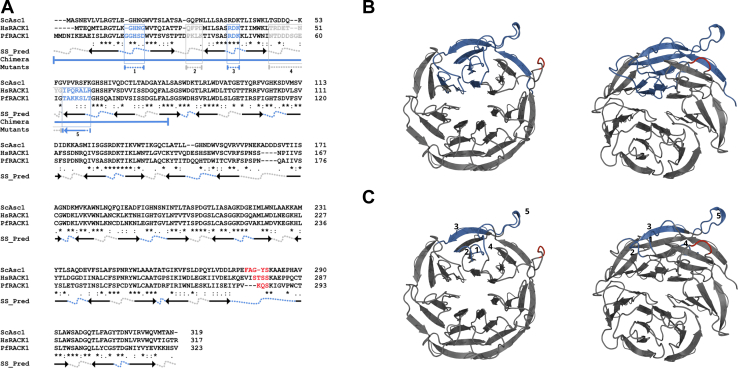
Figure 2.
Comparative bioinformatic analysis of RACK1 homologs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ScAsc1), Homo sapiens (HsRACK1), and Plasmodium falciparum (PfRACK1) homologs.A, sequence alignment of yeast Asc1, human RACK1, and Plasmodium falciparum RACK1 amino acid sequences generated by Clustal Omega. The SS_Pred is the secondary structure prediction using MPI Bioinformatics toolkit Quick2D tool. Arrows: beta strands. Arrows represent beta strands, with heads pointing from the N-terminal to C-terminal direction showing the orientation of the beta strand in the β-propeller. Dotted lines represent loops found between beta strands where gray notates solvent-facing loops and blue indicates ribosome-facing loops. Chimera (χ): proteins generated by region exchanged between human and parasite RACK1 proteins shown in solid blue lines. RDK→DDE mutant is indicated in blue text and blue dashed line. Clustal Omega consensus symbols: Asterisks (∗) indicates fully conserved residue. Colon (:) indicates conservation between residues of strongly similar properties (approximation of > 0.5 in the Gonnet PAM 250 matrix). Period (.) indicates conservation between residues of weakly similar properties (approximation of =< 0.5 and > 0 in the Gonnet PAM 250 matrix). B and C, a SWISS-MODEL generated de novo model of PfRACK1 displaying (B) chimeric region and (C) variable regions in blue. Left: Ribosome-facing surface. Right: 25-degree rotation. RACK1, receptor for activated C-kinase 1.