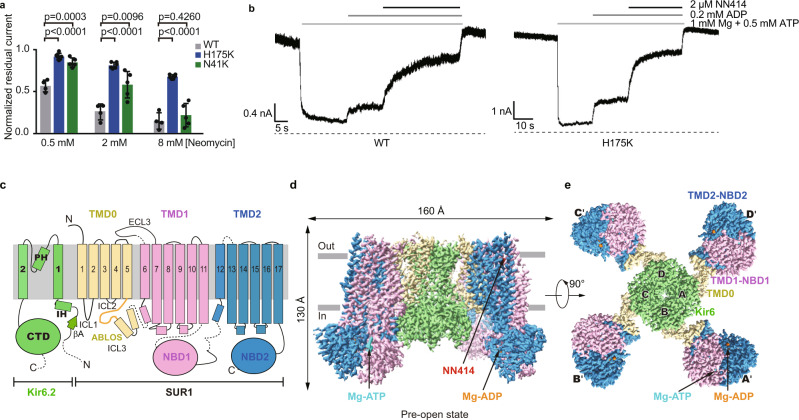
Fig. 1. Structure of the pancreatic KATP channel (H175Kcryo-EM) in the pre-open state.
a Neomycin inhibition of the inside-out currents of the KATP channel. Wild type (WT), H175K, and N41K mutants of Kir6.2 were co-expressed with wild type SUR1 for recordings. Data are shown as mean ± SD. WT n = 4, H175K n = 6, N41K n = 5 independent patches, respectively. p values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed t-test and were indicated above. b Representative inside-out recordings of KATP channel formed by the wild-type Kir6.2 or the H175K mutant. c Topology of Kir6.2 and SUR1 subunits. PH, pore helix; ECL, extracellular loop; ICL, intracellular loop; IH, interfacial helix; CTD, cytoplasmic domain; TMD, transmembrane domain; NBD, nucleotide-binding domain. Transmembrane helices are shown as cylinders. The phospholipid bilayer is shown as thick gray lines. Kir6.2, SUR1 TMD0-ICL3 fragment, TMD1-NBD1, and TMD2-NBD2 are shown in green, yellow, violet, and blue, respectively. d Side view of the KATP complex in the pre-open state. Mg-ADP, Mg-ATP, and NN414 are shown in orange, cyan, and red, respectively. e Bottom view of the KATP channel in the pre-open state from the intracellular side. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.