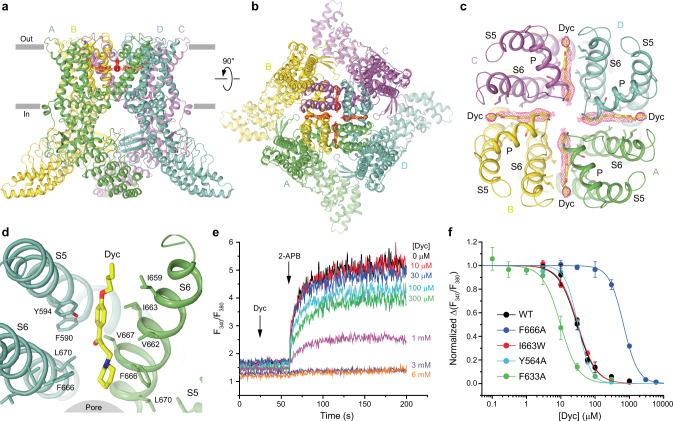
Fig. 2. TRPV3Dyc structure and dyclonine binding sites.
a, b TRPV3Dyc structure viewed from the side (a) or top (b), with subunits colored green, yellow, purple, and cyan. Red mesh shows densities for dyclonine. Dyclonine molecules are shown as sticks. c, d Close-up views of all four dyclonine binding sites (c) and only one of them (d). e Representative ratiometric fluorescence measurements of changes in intracellular Ca2+ for HEK 293 GnTI− cells expressing F666A mutant TRPV3 channels. The changes in the fluorescence intensity ratio F340/F380 were monitored in response to the addition of 200 µM 2-APB (arrow) after pre-incubation of cells with various concentrations of dyclonine. The experiment was repeated independently three times with similar results. f Dose–response curves for inhibition of wild-type and mutant TRPV3 channels by dyclonine. The changes in the fluorescence intensity ratio F340/F380 evoked by addition of 200 µM 2-APB after pre-incubation with various concentrations of dyclonine were normalized to their maximal values in the absence of dyclonine. Curves through the points are logistic equation fits, with IC50 = 29.8 ± 5.3 µM and nHill = 1.61 ± 0.27 (n = 7 independent experiments) for wild-type TRPV3, IC50 = 673 ± 37 µM and nHill = 2.07 ± 0.08 (n = 3 independent experiments) for F666A, IC50 = 31.5 ± 1.6 µM and nHill = 1.63 ± 0.07 (n = 3 independent experiments) for I663W, IC50 = 31.5 ± 1.0 µM and nHill = 2.33 ± 0.11 (n = 4 independent experiments) for Y564A and IC50 = 9.8 ± 0.7 µM and nHill = 1.68 ± 0.19 (n = 6 independent experiments) for F633A. Source data are provided.