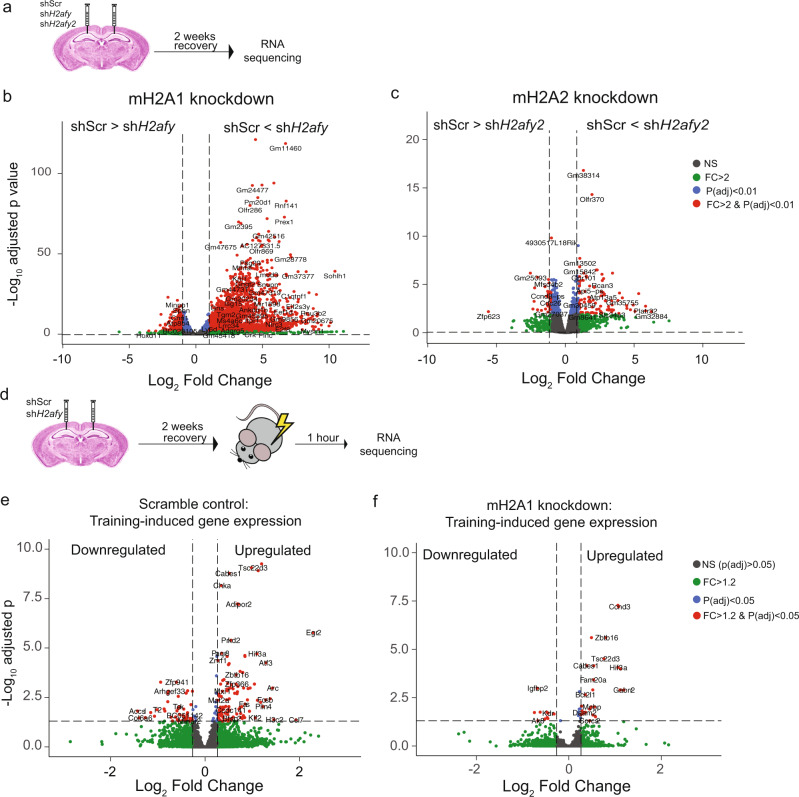
Fig. 2. mH2A1 depletion promotes basal gene expression and blocks learning-induced gene induction.
a Experimental design. Mice underwent stereotaxic surgery for intra-hippocampal (CA1) injections of AAV-DJ vectors carrying shRNA constructs against a scramble control sequence, H2afy or H2afy2. After 2 weeks of recovery, the infected region was extracted and RNA was sequenced. b Intra-CA1 depletion of H2afy (encodes mH2A1) alters the hippocampal expression of 2350 genes, majority of which (85%) were upregulated (significance cut-off: p adj < 0.01 and FC > 2). c Intra-CA1 depletion of H2afy2 (encodes mH2A2) alters the expression of 127 genes, 69% of which were upregulated (significance cut-off: p adj < 0.01 and FC > 2). d Experimental design for testing the effects of mH2A1 depletion on training-induced gene expression. Mice underwent stereotaxic surgery for intra-CA1 injections of shScr or shH2afy and were given 2 weeks to recover. After 2 weeks, half of the mice were fear conditioned and half were left undisturbed in their home cage. RNA was extracted from infected tissue and gene expression was compared in trained vs untrained mice for each virus. e In area CA1 of the hippocampus of scramble control mice, fear conditioning altered the expression of 169 genes, 122 of which were upregulated (significance cut-off: p adj < 0.05 and FC > 1.2). f In area CA1 of the hippocampus of mH2A1-depleted mice, fear conditioning altered the expression of 44 genes, 33 of which were upregulated (significance cut-off: p adj < 0.05 and FC > 1.2). n = 3 mice/group.