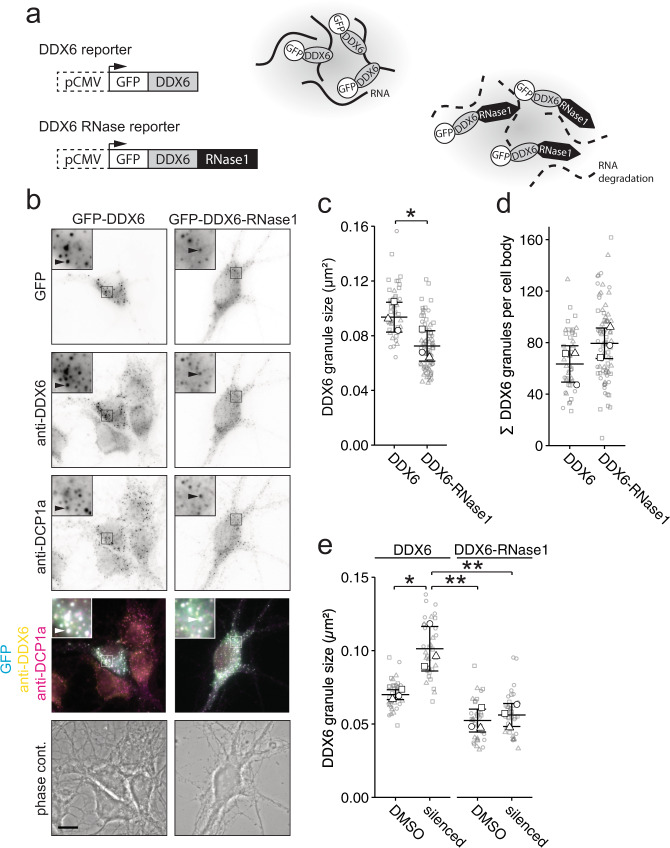
Fig. 5. RNA degradation in DDX6 granules results in disassembly.
a Scheme of GFP-DDX6 and GFP-DDX6-RNase1 expression cassettes (right) and their use in an RNA-dependent assembly assay (left). b Representative examples of GFP fluorescence, anti-DDX6 and anti-DCP1a immunofluorescence, merge, and phase contrast pictures of 14 DIV hippocampal neurons in culture, transfected with either GFP-DDX6 or GFP-DDX6-RNase1 reporters. Boxed regions in images are displayed as magnified insets. Scale bars 10 µm. Arrowheads indicate overlap. c, d, e Dot plots displaying average DDX6 granule size (c, e) or DDX6 granule number (d) of individual cell bodies as exemplified in b, transfected with either GFP-DDX6 or GFP-DDX6-RNase1 reporters (c, d) and under vehicle treated or silenced conditions (e). Distinct dot symbols indicate biological replicates. Small gray symbols represent single cells while larger white symbols indicate the average of each replicate. Horizontal line and error bars represent mean of replicates and standard deviation (n = 3 biologically independent experiments). Asterisks represent p-values obtained by two-sided Student’s t-test (c, d) or Tukey’s test post-hoc to one-way ANOVA analysis (e) (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). p = 0.0306 (c), F1,8 = 0.00045, GFP reporter; F1,8 = 0.0128, neuronal inhibition (e).