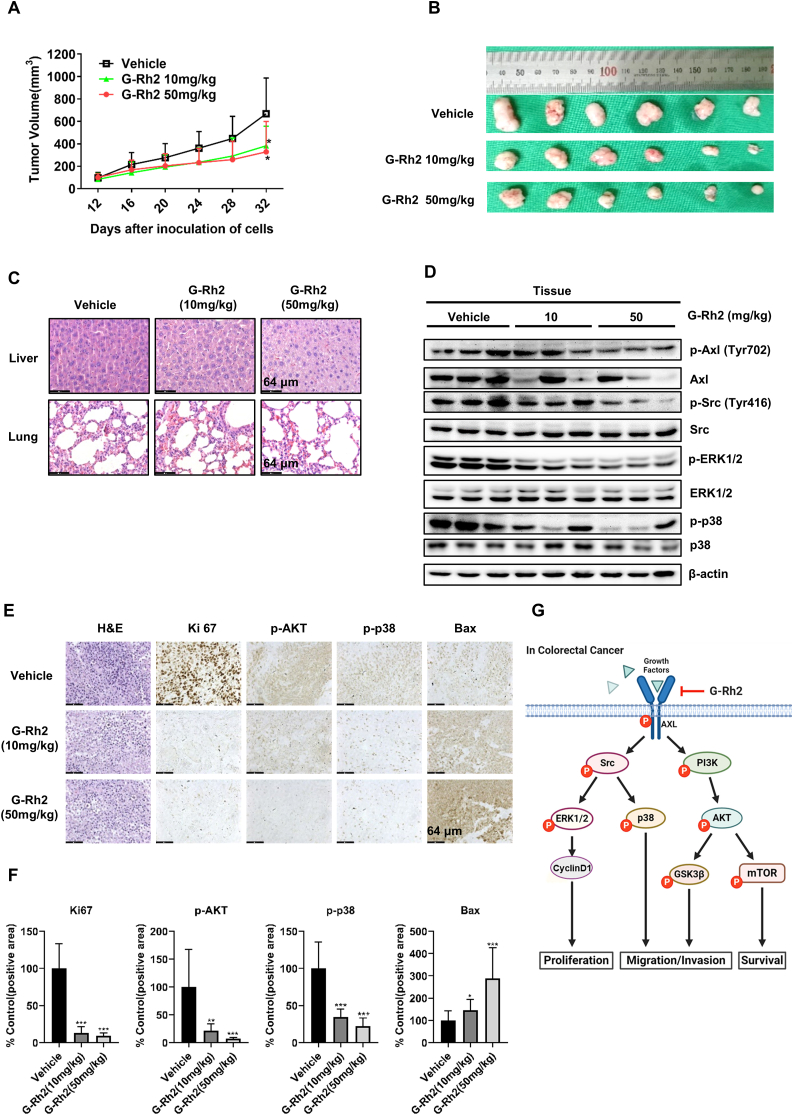
Fig. 6.
G-Rh2 suppresses HCT116 cell xenograft tumor growth in nude mice. (A) Tumor growth curve was plotted according to the tumor volume and the day after treatment. Data shown are means ± SDs of tumor volume for each group (n = 6). (B) Images of tumor size in three groups excised from the mice on the 32 nd day after implantation. (C) The expression of p-Axl, Axl, p-Src, Src, p-ERK1/2, ERK1/2, p-p38, and p38 in tumor tissues was measured by western blotting. (D) H&E staining of liver and lung specimens collected from mice. (E) and (F) Immunohistochemical analysis of Ki-67, p-AKT, p-p38, and Bax in xenograft tumors tissues. (G) Schematic diagram of the underlying mechanism of the G-Rh2 effects on CRC cells. G-Rh2 binds to Axl and suppresses the Axl signaling pathway, thus inhibiting CRC cell growth, migration, and invasion. Scale bar, 64 μm. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 versus control.