Figure 4.
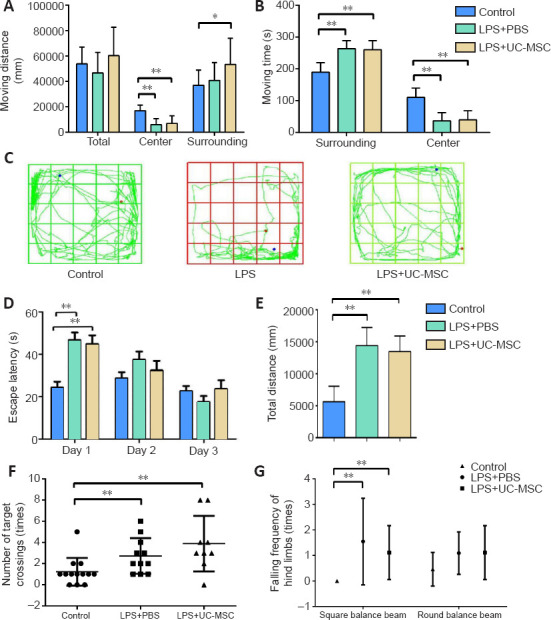
Effect of UC-MSCs on behavioral tests of neonatal rats with maternal immune activation-associated neonatal brain injury.
(A–C) The movement distance (total, center, surrounding) (A), total moving time (B), and movement trajectory (C) in the open field test. Blue dots indicate the starting point of the test, red dots indicate the end point of the test, and green lines indicate the trajectory. (D) Escape latency in the Morris water maze training stage on the training days. (E) The total distance to search for the platform in the Morris water maze formal test on the fourth day. (F) The number of successful platform crossings in the Morris water maze formal test. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (control: n = 13, LPS + PBS: n = 11, LPS + UC-MSC: n = 9). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (one-way analysis of variance followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls method). (G) The number of drops of left or right leg in the square/round balance beam test. LPS: Lipopolysaccharides; MWM: Morris water maze; PBS: phosphate-buffered saline; UC-MSCs: umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
