Figure 8.
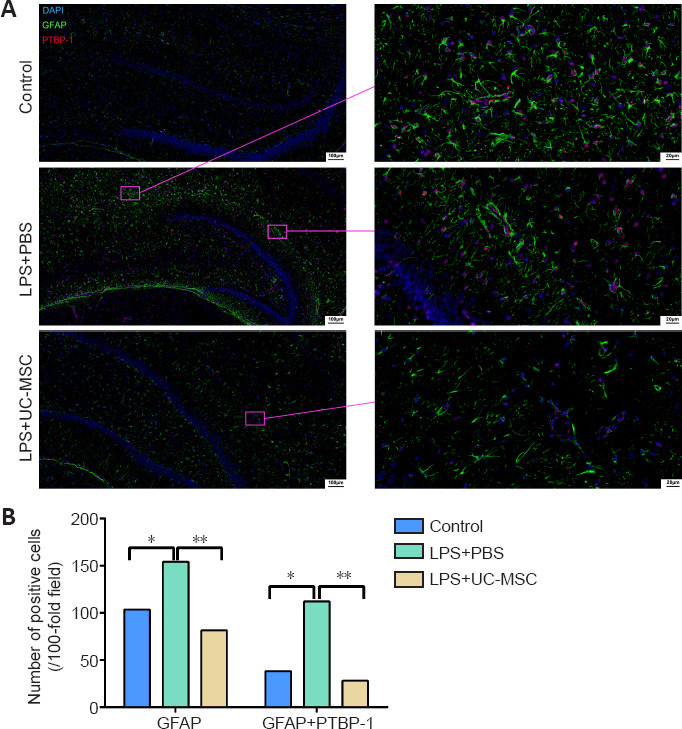
Effect of UC-MSCs on the distribution of GFAP and PTBP-1-positive cells in the hippocampus of neonatal rats with maternal immune activation-associated neonatal brain injury.
(A) Immunofluorescence images of the distribution of PTBP-1 (red, stained with Alexa Fluor 647) and GFAP (green, stained with FITC) positive cells in the hippocampus. The number of GFAP-positive/PTBP-1-positive cells in the LPS + PBS group was significantly higher than that in the control group, showing a linear arrangement. In the LPS + UC-MSC group, the number of GFAP-positive/PTBP-1-positive cells was lower than that in the LPS + PBS group. Linear arrangement was still observed, but the arrangement was looser. After LPS injury, PTBP-1 was expressed in the nucleus of the injured neurons, and GFAP surrounded the PTBP-1-positive cells. Scale bars: 100 μm (left), 20 μm (right). (B) Quantitative results of the number of GFAP-positive cells and PTBP-1/GFAP-positive cells in the hippocampus. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (one-way analysis of variance followed by Student-Newman-Keuls method). DAPI: 4′, 6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole; DG: dentate gyrus; GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein; LPS: lipopolysaccharides; PBS: phosphate-buffered saline; PTBP-1: polypyrimidine tract-binding protein-1; TUJ-1: neuron-specific class III β-tubulin; UC-MSCs: umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
