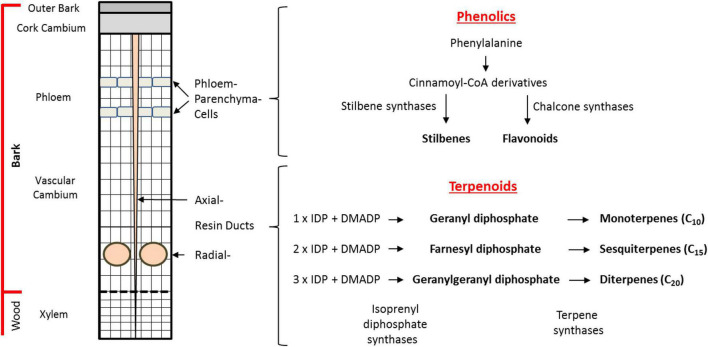
FIGURE 1.
Biosynthesis and storage of defense compounds in Norway spruce bark. Depicted on the left is a schematic cross section of the cambial region of the trunk of a mature tree. Phenolic compounds are localized in bands of phloem parenchyma cells in the phloem. Terpenoid resin compounds are localized in radial resin ducts in the xylem and in axial resin channels that traverse both the xylem and phloem. An outline of the biosynthetic pathways to terpene and phenolic defense compounds is given on the right. The major phenolic compounds (stilbenes, flavonoids) are synthesized in the phloem parenchyma cells from phenylalanine with stilbene synthases (STSs) and chalcone synthases (CHSs) being the key branchpoint enzymes. The terpenoid resin compounds are synthesized in the epithelial cells lining the resin ducts from the C5 units isopentenyl diphosphate (IDP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMADP). The isoprenyl diphosphate synthases catalyze the formation of the intermediates geranyl diphosphate (GDP), farnesyl diphosphate (FDP), and geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGDP). These intermediates are converted into monoterpenes (C10), sesquiterpenes (C15), and diterpenes (C20), respectively, by the action of terpene synthases (TPSs).