Fig. 4.
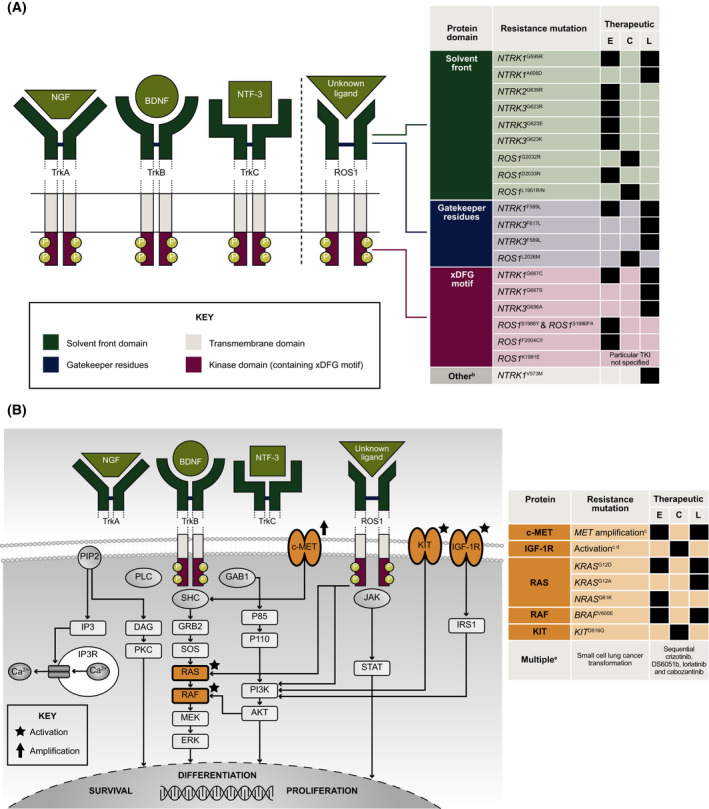
Mechanisms of acquired resistance to TKIs in NTRK‐fp solid tumours and ROS1‐fp NSCLC: (A) On‐target resistance; (B) Off‐target resistance. Black square indicates clinical resistance observed following treatment with therapeutic. aDual mutation. bFunctional domain/structure not reported/unknown. cSpecific mutation unknown/not reported. dReported in patients with ALK fusion‐positive lung cancer only. eComplete genomic profile of transformed SCLC not fully elucidated. ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; BDNF, brain‐derived neurotrophic factor; C, crizotinib; DFG, Asp‐Phe‐Gly motif; E, entrectinib; KIT, KIT proto‐oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase; KRAS, Kirsten rat sarcoma virus; L, larotrectinib; MET, mesenchymal epithelial transition; NGF, nerve growth factor beta; NRAS, neuroblastoma RAS viral (v‐ras) oncogene homolog; NTF‐3, Neurotrophin‐3; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; Trk, tropomyosin receptor kinase.
