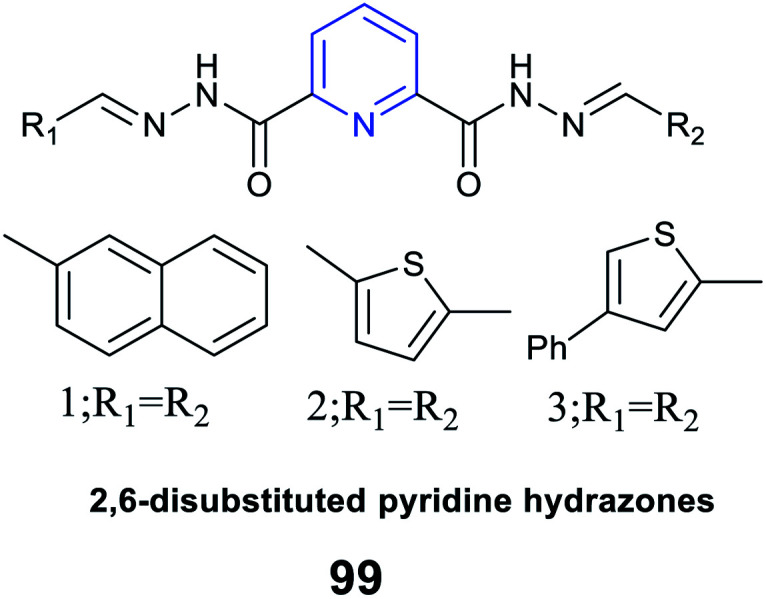
|
Cytotoxic activity against HT-29 cell line |
IC50 = 6.78, 8.88 and 8.26 μM respectively |
Morphological changes of HT-29 and ISH cells and caspase-3 activation |
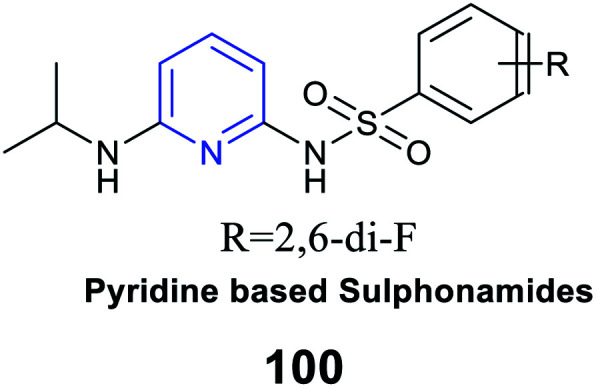
|
Antidiabetic action |
IC50 of alpha amylase inhibition is 54.18 ± 0.150 μg mL−1
|
Inhibition of α-amylase |
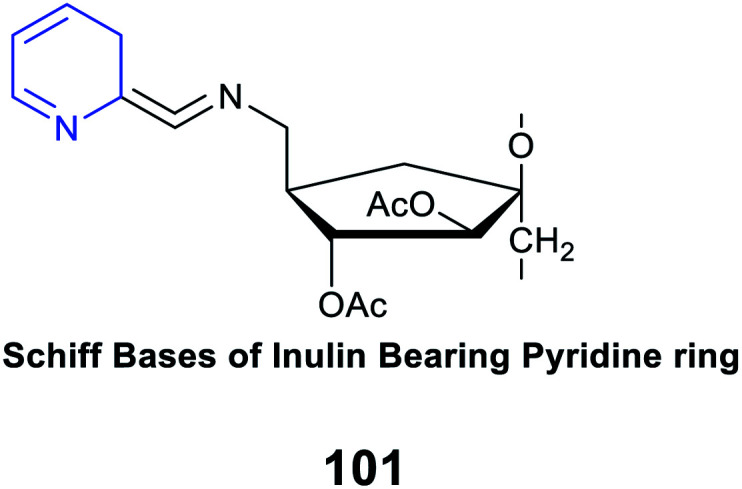
|
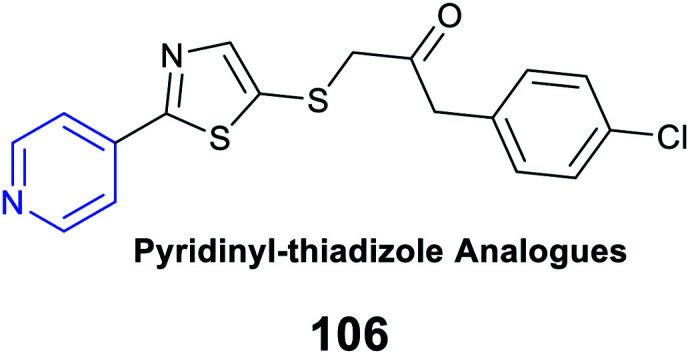
Antifungal activity |
An inhibitory index of 77.0% against botrytis cinerea at 2.0 mg mL−1
|
Interaction with anionic components of the cell membranes, i.e., glucan, mannan, proteins, and lipids, to destroy the cell membranes or to form an impervious layer preventing the transport of essential nutrients from entering the cell |
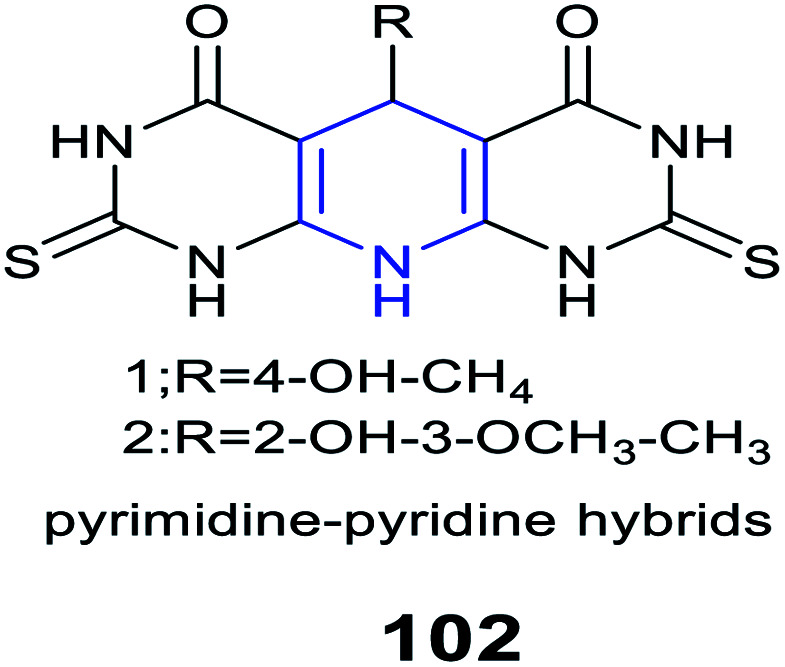
|
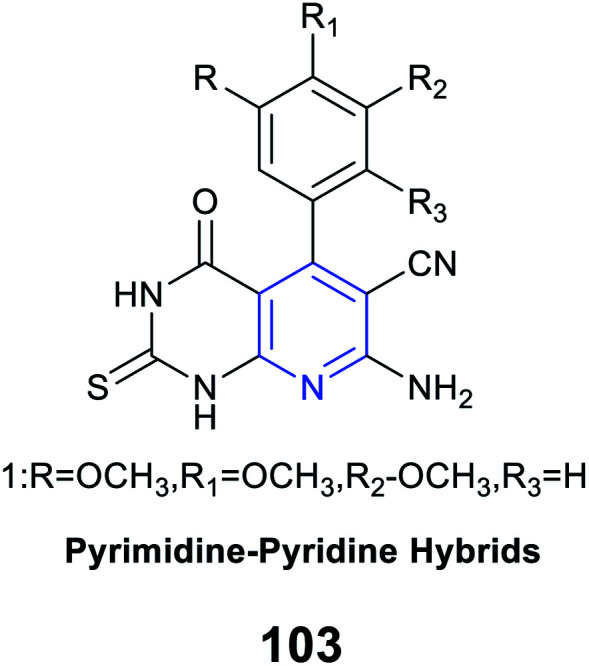
Anti-inflammatory activity |
COX-2 inhibitory activity in a range (IC50 = 0.25–0.89 mM) |
Competitive selective COX-2 inhibitors |
|
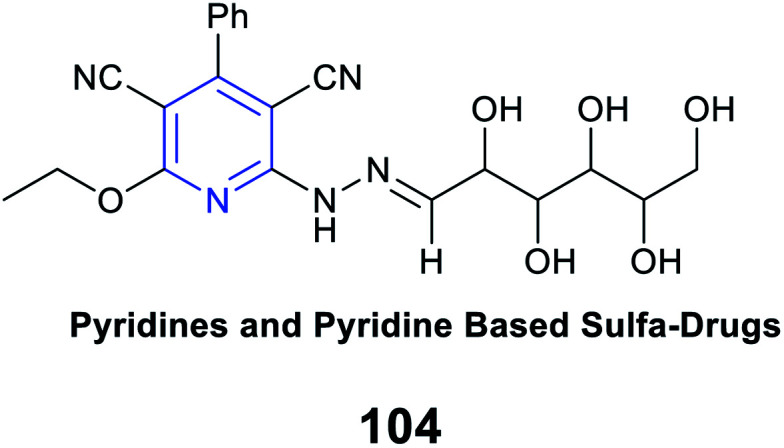
Ulcerogenic liability |
High COX-2 selectivity with COX-2 S.I. = 17.08 |
Competitive selective COX-2 inhibitors |
|
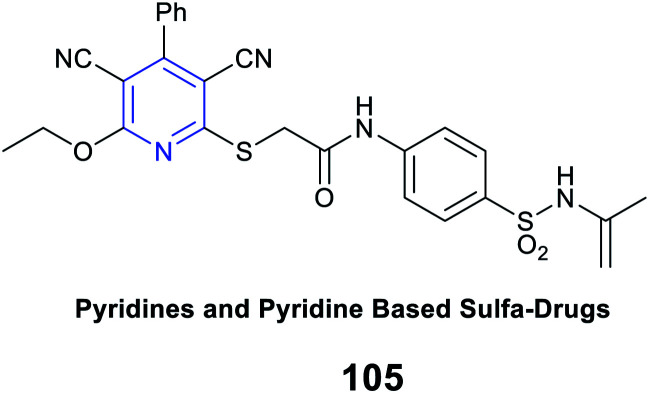
Antimicrobial activity |
ZOI value 34 mm (more than the standard drug cefotaxime) against E. coli
|
Cell wall disruption |
|
Antimicrobial activity |
ZOI value 34 mm (more than the standard drug cefotaxime) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
High cell permeability efficacy |
|
Antitubercular activity |
Inhibitory activity of 0.06 μM against the MDR H37RV strain |
Inhibition of RNA synthesis |
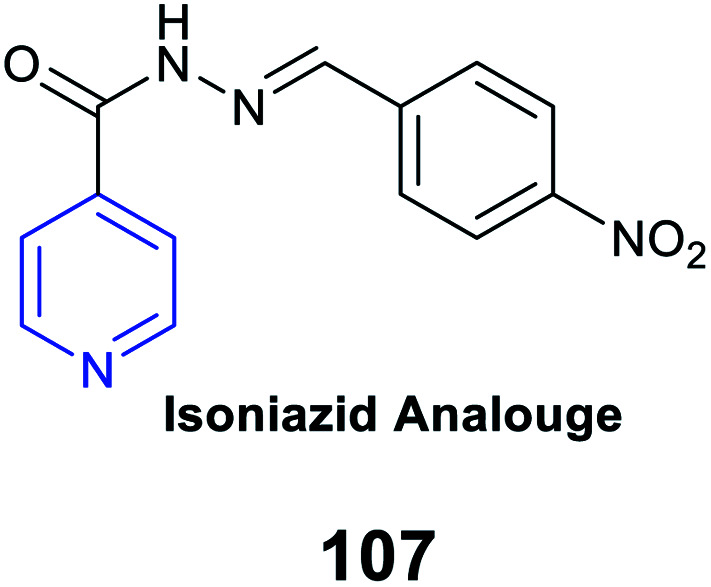
|
Antitubercular activity |
Antimycobacterial activity of 1.2 μg mL−1 against the MTB H37RV strain |
Strong binding to the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
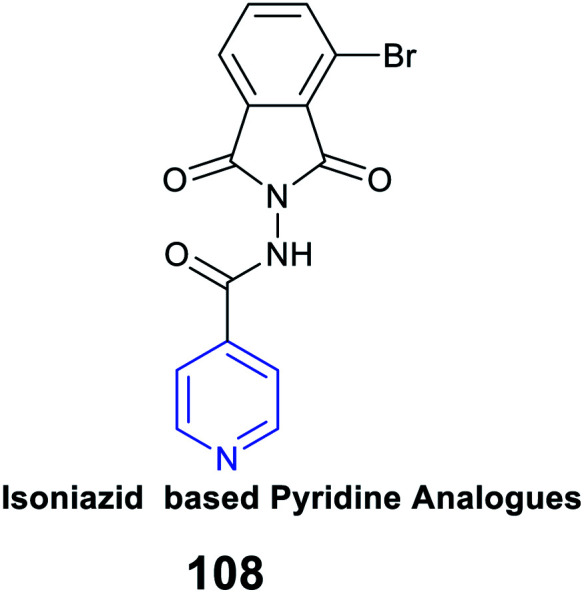
|
Antimycobacterial activity |
IC50 of 3.2 μM against the H37Rv strain |
Inhibition of RNA synthesis |
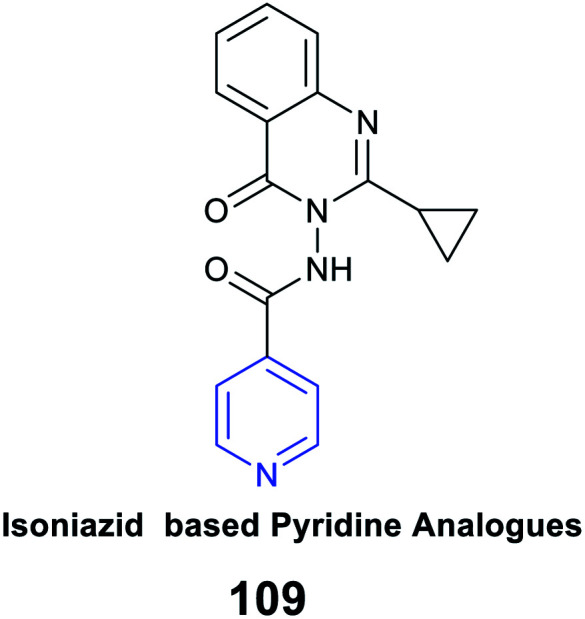
|
Antimycobacterial activity |
IC50 of 1.5 μM against the H37Rv strain |
Inhibition of RNA synthesis |











