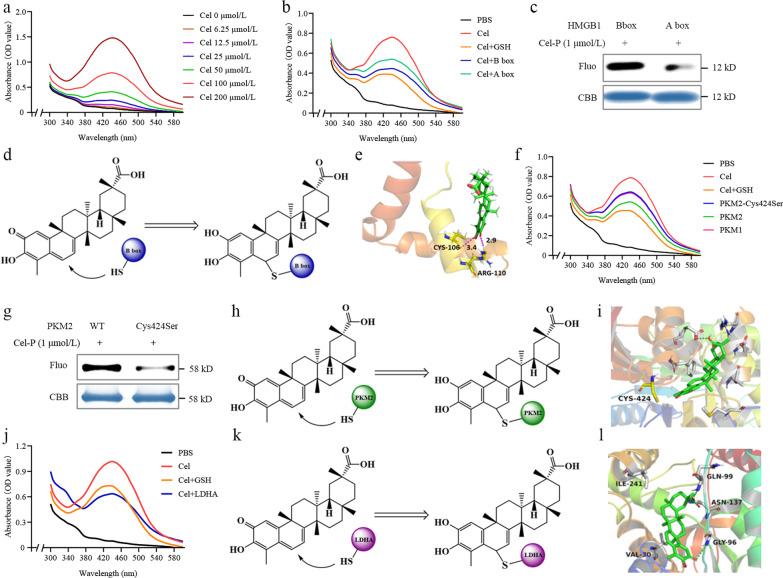
Fig. 7.
Celastrol (Cel) reacts with Cys residues in PKM2 and HMGB1 to inhibit their activities. a Absorption spectra of Cel at 6.25–200 μmol/L. b Absorption spectra of 100 μmol/L Cel in the presence or absence of GSH, HMGB1 A box, or B box. c Fluorescence intensity of recombinant A box and B box incubated with celastrol-probe (Cel-P) and then click-reacted with a fluorescent dye. d Scheme depicting Cel binding to B box. e Molecular docking model of Cel binding to HMGB1. f Absorption spectra of 100 μmol/L Cel in the presence or absence of GSH, PKM1, wild-type PKM2, or PKM2-Cys424Ser. g Fluorescence intensity of recombinant wild-type PKM2 and PKM2-Cys424Ser incubated with Cel-P and then click-reacted with a fluorescent dye. h Scheme depicting Cel binding to PKM2. i Molecular docking model of Cel binding to PKM2. j Absorption spectra of 100 μmol/L Cel in the presence or absence of GSH and LDHA. k Scheme of Cel binding to LDHA. l Molecular ducking model of Cel binding to LDHA. PBS phosphate-buffered saline, GSH glutathione, LDHA lactate dehydrogenase A, PKM2 pyruvate kinase M2, HMGB1 high mobility group box 1, Fluo fluorescence, CBB coomassie brilliant blue