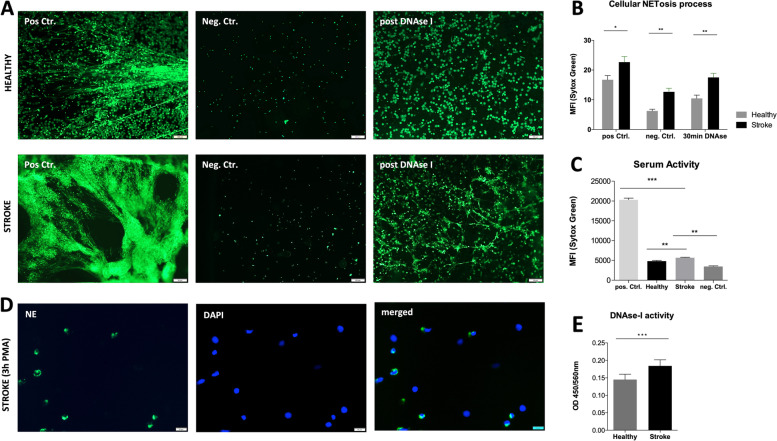
Fig. 3.
Neutrophils of stroke patients show elevated NET formation with worse resolution of already formed NET. A Representative images of neutrophils with or without NET formation for control patients (Healthy; upper row; n = 16) and stroke patients (Stroke; lower row; n = 35) Neutrophils are isolated from peripheral blood via ficoll density gradient and plated. NET formation is triggered by adding of 100 mM PMA (positive control) or DMSO (negative control) for 3 h. For the DNase-I control, samples are treated with 100 mM PMA for 3 h and afterwards with DNase-I for 30 min. Sytox Green is added to all samples 10 min before fixation with 4% PFA. NET formation is determined directly after fixation. B Quantification of the MFI (mean fluorescence intensity) of the Sytox Green positive images show significantly higher NET formation for patients with ischemic stroke for the positive control, but also already in resting neutrophils (negative control) and a worse resolution of NET upon DNAse-I treatment. C Neutrophils treated with serum of patients with ischemic stroke (3rd bar; n = 35) as well as serum of controls (2nd bar; n = 16) show significantly higher NET formation determined via MFI in comparison to the positive control (100 ng PMA) and the negative control (DMSO). D Represantative images of PMA stimulated neutrophils, showing nuclear expression (DAPI) of neutrophil elastase (NE) in green (anti-NE FITC) upon NETosis. E Serum of patients with ischemic stroke (3rd bar; n = 35) as well as serum of controls (2nd bar; n = 16) is analyzed for DNase-I levels and reveals higher levels of the enzyme in sera derived from stroke patients (p < 0.001). Data are representative of independent experiments with 35 stroke patients and 16 control patients (Healthy) and presented as mean ± SEM. Abbreviations: NET, neutrophil extracellular traps; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. Mann-Whitney-U Test, * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001