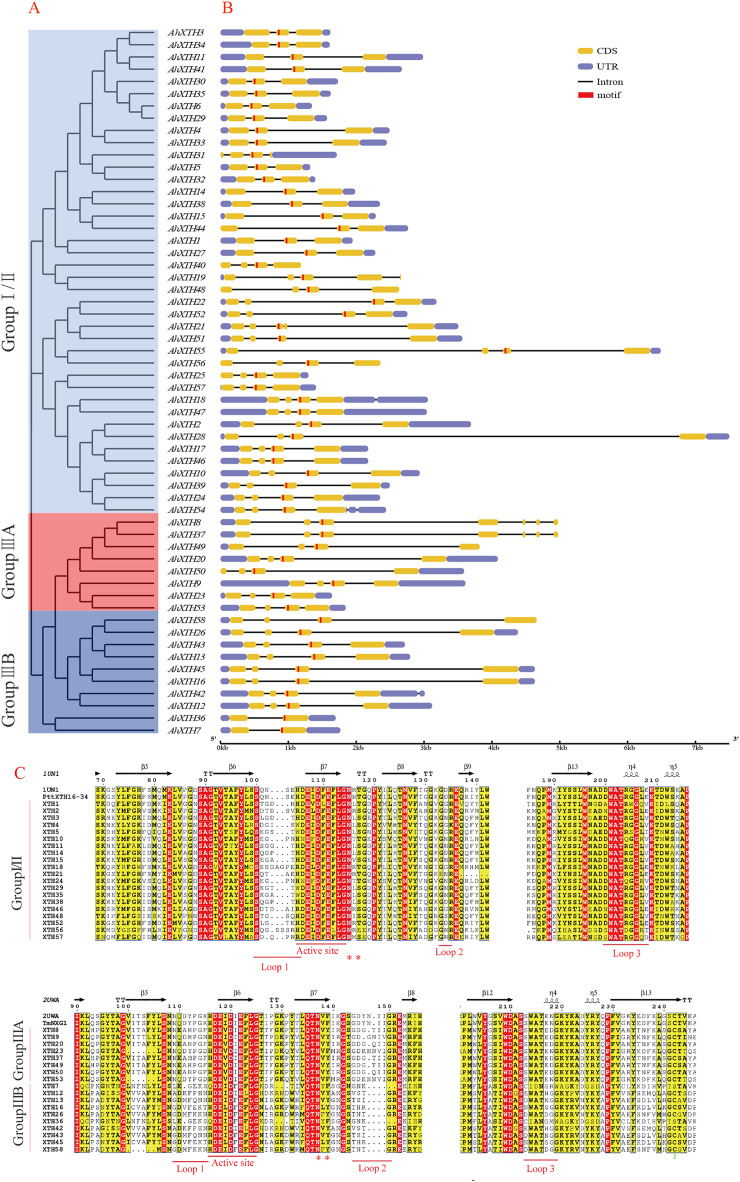
Figure 4. Structure analysis of AhXTH genes and identification of conserved domain of their encoded proteins.
(A) The unrooted phylogenetic tree of 58 peanut AhXTHs; (B) The exon–intron structure of peanut AhXTH genes. The coding sequences (CDS) and the untranslated regions (UTR) were indicated by yellow boxes and blue boxes. The boxes in red color highlighted the active site of AhXTHs; (C) Multiple alignment of partial amino acid sequences of peanut AhXTHs for showing the conserved secondary structures. Amino acid sequences were aligned using PttXET16-34 (1UN1) and TmNXG1(2UWA) as the referent sequences by MEGA X, and their secondary structures were predicted using ESPript. The conserved residues were shown in grey frames, among which the identity residues were indicated by white letters in red boxes, and the similar residues by black letters in yellow boxes. The secondary structures of β sheets and α-helices were shown on the top of sequences with arrows and spirals. The conserved catalytic domain (DEIDFEFLG), and loops 1, 2 and 3 were indicated using red lines on the bottom of sequences. N-glycosylation residues were indicated as asterisks. (The alignment results of intact amino acid sequences of 58 AhXTHs was presented in Files S5 and S6)