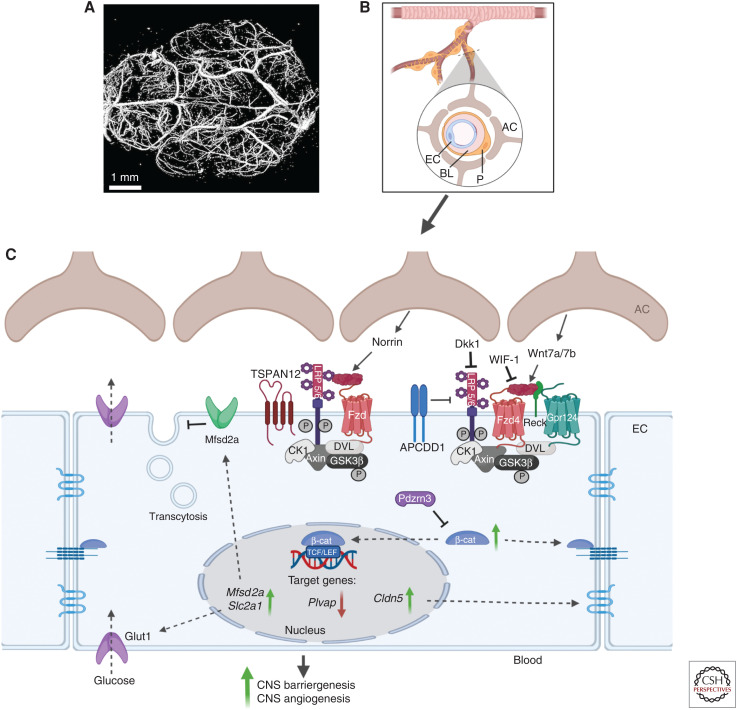
Figure 3.
The Wnt signaling pathways in central nervous system (CNS) blood vessels. (A) Mouse brain vasculature was imaged with a high-resolution micro-computed tomography (CT) imaging system (Bruker MicroCT). Scale bar, 1 mm. (B) The blood-brain-barrier (BBB) creates a physical interface between blood and brain tissue. The interactions between endothelial cells (ECs), pericytes (Ps), and astrocytes (ACs) form the neurovascular unit in the CNS and are crucial for the formation and maintenance of the BBB. The BBB is characterized by microvascular ECs, which display unique properties linked to their barrier function, including specialized tight junctions, a lack of fenestration, a selective nutrient and efflux transporters system, and a low rate of transcytosis. (C) The canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling has a major role during CNS barriergenesis and angiogenesis. Activation of the pathway involves the Norrin ligand produced by astrocytes and the downstream activation of a receptor complex formed by Fzd, LRP5/6, and Tetraspanin12. Alternatively, Wnt ligands (Wnt7a/b) secreted by astrocytes can also bind to the receptor complex consisting of Fzd and LRP5/6, which then recruits the DVL protein to the plasma membrane and induces β-catenin stabilization and its accumulation in the cytoplasm. The ubiquitin ligase PDZRN3 can block this process. Other receptors and coreceptors (probable G-protein-coupled receptor 124 [Gpr124] and reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs [Reck]) can enhance this Wnt-dependent signaling pathway, while the Wnt modulator adenomatosis polyposis coli down-regulated 1 protein (APCDD1) can block it. Inhibitors of Wnt ligands (Wnt inhibitory factor 1 [WIF-1]) or of coreceptors LRP5/6 (Dickkopf [Dkk1]) also contribute to the blocking of Wnt signaling. Stabilized β-catenin can then either contribute to the adherens junction at the plasma membrane or translocate to the nucleus and stimulate the transcription of target genes such as claudin 5 (Cldn5), which then contributes to the formation of tight junctions. Wnt/β-catenin signaling also increases the expression of solute carrier family 2 member 1 (Slc2a1), which is a specialized glucose transporter encoding for Glut1 protein and induces the expression of major facilitator superfamily domain-containing protein 2A (Msfd2a), which inhibits transcytosis. Created with BioRender.com. (BL) Basal lamina, (Plvap) plasmalemma vesicle-associated protein.