Figure 4.
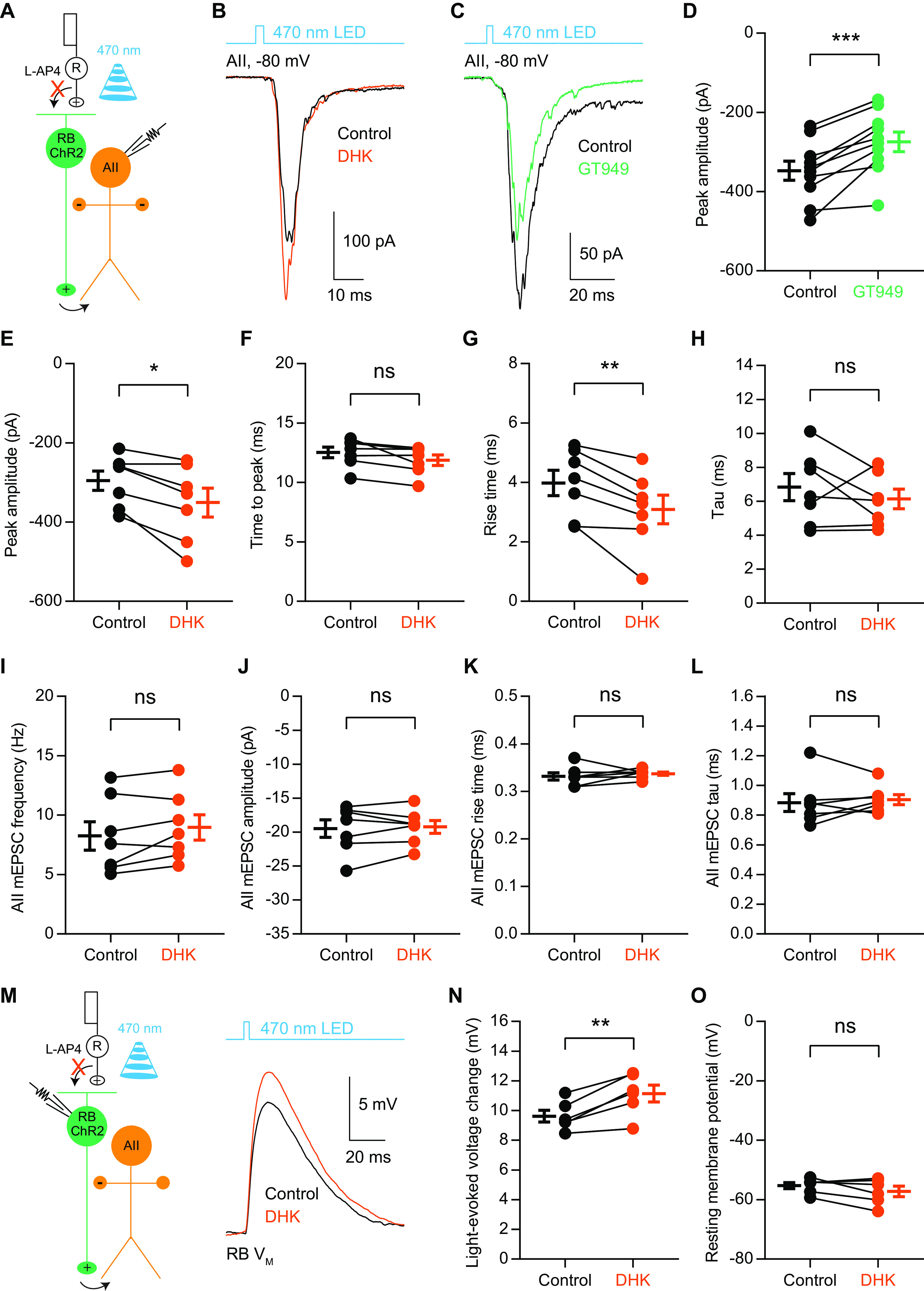
EAAT2 regulates signal transmission at RB→AII ribbon synapses. A, A schematic diagram showing the optogenetic study of neurotransmission between RBs and AII amacrine cells. ChR2 was expressed predominantly in RBs by cre-dependent recombination in adult Pcp2-cre::Ai32 mouse retinas. With all the synaptic transmission between photoreceptors and BCs is blocked pharmacologically, brief flashes of 470-nm LED light can directly activate ChR2+ RBs and induce postsynaptic responses in AIIs, which mainly reflect neurotransmitter release from RBs. The electrical coupling between ChR2+ ON cone bipolar cells and AIIs is negligible under this experimental condition (Liang et al., 2021). R, rod. B, The EPSCs recorded in AIIs, which were evoked by 470-nm LED light stimulation, were enhanced by 200 μm DHK, a selective EAAT2 blocker. Vhold = −80 mV. C, The ChR2-evoked EPSCs were reduced by 10 μm GT949, a positive allosteric modulator of EAAT2. D, E, Summary data showing the effects of GT949 (n = 10) and DHK (n = 7) on the peak amplitude of AII EPSCs. F, DHK reduced the time to peak of EPSCs slightly, but not significantly (n = 7, p = 0.0531). G, DHK reduced the rise time of EPSCs (n = 7). H, DHK did not change the decay time (tau) of EPSCs (n = 7). I–L, DHK did not affect the frequency, amplitude, rise time, or tau of mEPSCs recorded in AIIs (n = 7). mEPSCs, miniature EPSCs. M, The voltage changes in ChR2+ RBs, which were evoked by brief flashes of 470-nm LED light, were increased by 200 μm DHK. N, DHK increased the voltage changes in RBs evoked by light flashes (n = 6). O, DHK did not influence the resting membrane potentials of RBs (n = 6). The data were represented as mean ± SEM. Wilcoxon signed-rank test or Student’s t test was used where appropriate. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; ns, not significantly different. See also Table 4.
