FIGURE 4.
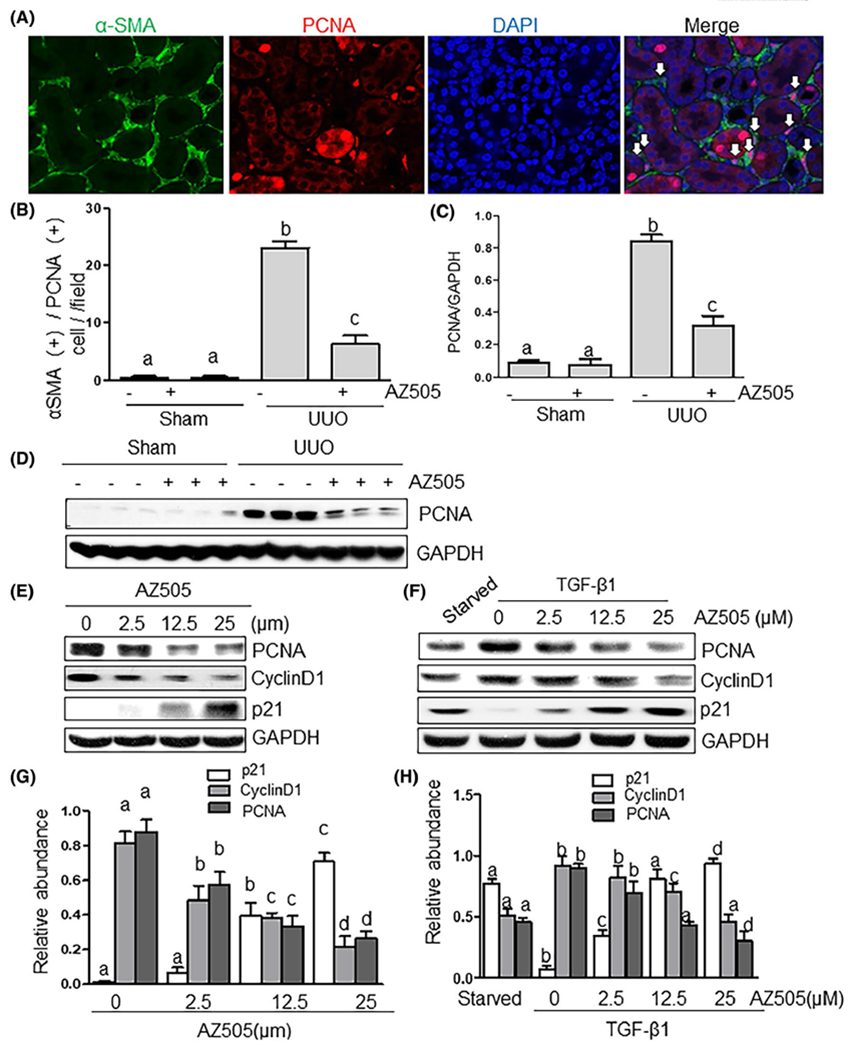
AZ505 inhibits cell proliferation in the kidney after UUO injury and in the culture of renal interstitial fibroblasts. A, Photomicrographs illustrating the kidney tissue stained with DAPI and antibodies against α-SMA and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) (magnification ×200). B, The α-SMA (+)/PCNA (+) cells in the interstitium were calculated in ten high-power fields and expressed as means ± SDs. White arrows indicate PCNA-positive myofibroblasts. Kidney tissue lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies against PCNA or GAPDH (D). Expression levels of PCNA were quantified by densitometry and normalized with GAPDH (C). NRK-49F cells were cultured in the DMEM with 5% FBS (E, G) or 2 ng/mL TGFβ1 (F, H) in the presence or absence of AZ505 at the doses as indicated for 36 hours. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies against PCNA, cyclin D1, p21, or GAPDH (E, F). Expression levels of PCNA, cyclin D1, p21, or GAPDH were quantified by densitometry, and the levels of PCNA, cyclin D1, p21 were normalized with GAPDH (G, H). Values are the means ± SDs of at least three independent experiments. Means with different letters (a-d) are significantly different from one another (P < .05)
