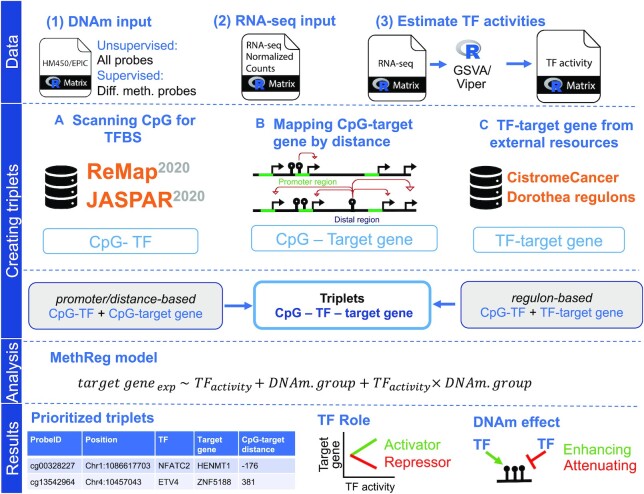
Figure 2.
Workflow of MethReg. Data: MethReg input datasets are (1) DNA methylation array data (HM450/EPIC) with beta values, (2) RNA-seq data with normalized counts and (3) estimated TF activities from the RNA-seq data using GSVA (gene set variation analysis) or VIPER (virtual inference by enriched regulon analysis) software. Creating triplets: There are multiple ways to create CpG–TF–target gene triplets. (A) A CpG can be mapped to TFs using TF motifs in databases such as JASPAR2020 or ReMap2020, by scanning the CpG location to identify whether it is close to a TFBS. (B) CpGs can be mapped to target genes using a distance-based approach. A CpG is linked to a gene if it is in the promoter region (< ±2 kb from the TSS). A distal CpG can be linked to either all genes within a fixed width (i.e., 500 kb) or a fixed number of genes upstream and downstream of the CpG location. (C) TF-target gene pairs can be retrieved from external databases (e.g., Cistrome Cancer and Dorothea). Using two different pairs (i.e., CpG–TF and TF–target gene), triplets can then be created. Analysis: Each triplet will be evaluated using a robust linear model, in which DNAm.group is a binary variable indicating whether a sample has high (fourth quartile) or low (first quartile) DNA methylation levels at the CpG. Results: MethReg outputs the prioritized triplets and classifies both the role of TF in the target gene expression (repressor or activator) and the role of DNA methylation on TF (enhancing or attenuating).