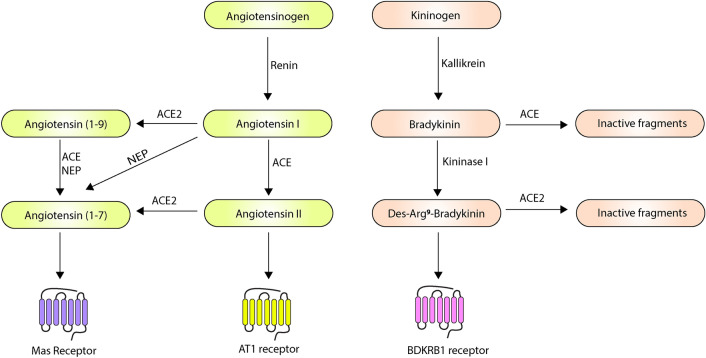
Fig. 4.
A schematic diagram of ACE2, ACE and Bradykinin regulation mechanisms. The enzyme ACE can act on Angiotensin I and Bradykinin to convert them into Angiotensin-(1–9) and inactive fragments, respectively, thus connecting the two pathways. The resulting products, Angiotensin-(1–7), Angiotensin II, and des-Arg9 bradykinin mediate their effects through Mas, AT1 and BDKRB1 receptors. (Notations: ACE- Angiotensin-converting enzyme, NEP- Neprilysin)