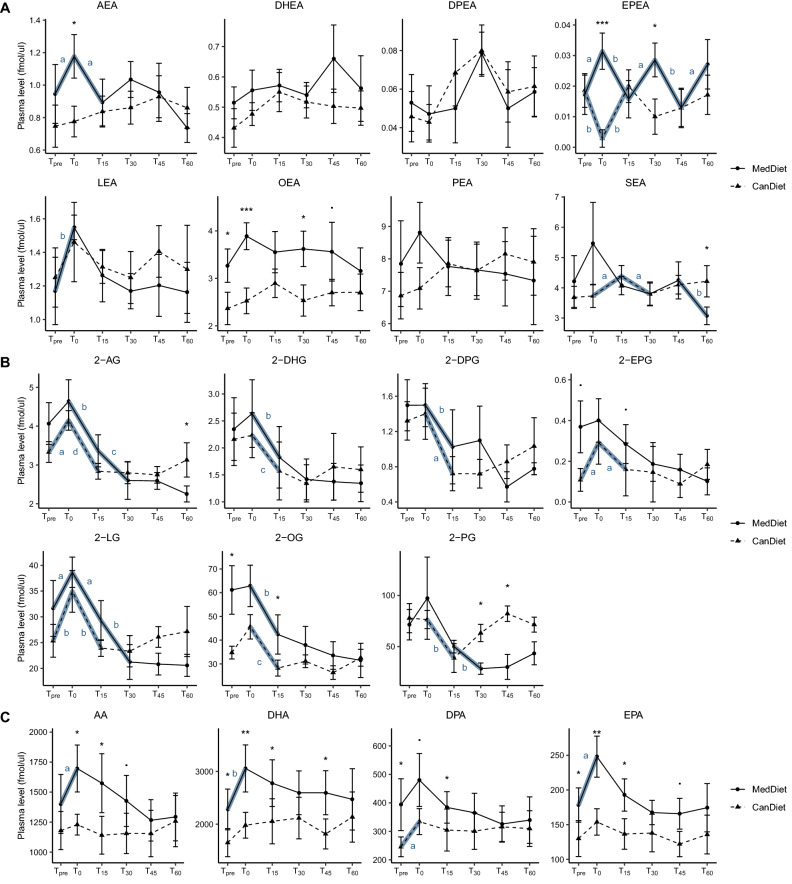
Figure 2.
Response curves of eCBome mediators and precursors (fmol/μl) to maximal aerobic test according to the diet. Panels show results for (A) N-acylethanolamines, (B) monoacylglycerols and (C) polyunsaturated fatty acids. The graph represents the mean with the standard error of the plasmatic concentrations of these lipids at each time point for the two diets. Tpre corresponds to the initial concentration before the aerobic test, T0 corresponds to the immediate end of the aerobic test and T15, T30, T45 and T60 correspond to the recovery phase. Lipid concentrations have been normalized using ranked values fitted into mixed linear-effect models (LME) and differences between diets and times have been tested by analysis of variance (ANOVA). For difference between diets, significance was set at p < 0.1 (.), p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**) and p < 0.001 (***). For difference between times, indicated by bold blue line, significance was set at p < 0.1 (a), p < 0.05 (b), p < 0.01 (c), p < 0.001 (d). N = 7 per diet. Names of the molecules are anandamide (AEA), N-palmitoylethanolamine (PEA), N-oleoylethanolamine (OEA), Nlinoleoylethanolamine (LEA), N-stearoylethanolamine (SEA), Ndocosapentaenoylethanolamine (DPEA), Neicosapentaenoylethanolamine (EPEA), Ndocosahexaenoyl‑ethanolamine (DHEA), 1- plus 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol (2-AG), 1- plus 2-palmitoyl-glycerol (2-PG), 1- plus 2-oleoyl-glycerol (2-OG), linoleoyl-glycerol (2-LG), 1- plus 2-eicosapentaenoyl-glycerol (2-EPG), 1- plus 2-docosaepentaenoic-glycerol (2-DPG), 1- plus 2-docosahexaenoyl-glycerol (2-DHG), arachidonic acid (AA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), docosapentaenoic acid (DPA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA).