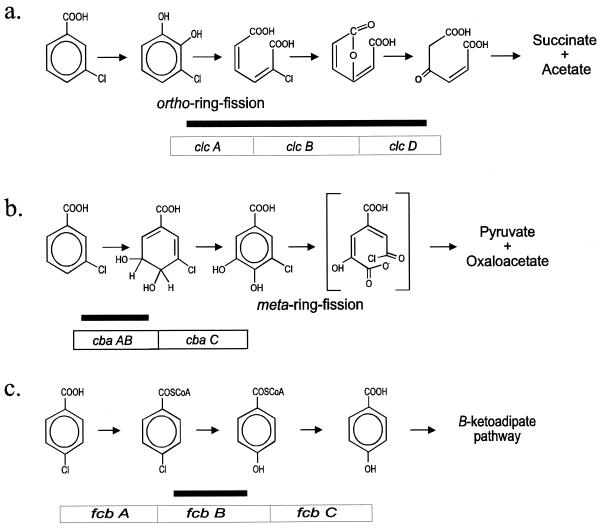
FIG. 1.
Representative metabolic pathways encoded by the nonhomologous CBA-degradative operons clcABD, cbaABC, and fcbBAC. The genes that make up these operons are indicated in open boxes below the metabolic steps they encode. Schematic representations of the locations of the three DNA probes used in this study, with respect to the operons, are shown as black bars. (a) Chlorocatechol ortho-ring-fission pathway. Following initial attack by a nonspecific dioxygenase such as the benzoate (benABC) or toluate (xylXYZ) dioxygenase and dihydrodiol dehydrogenase to form chlorocatechols, the clcABD gene products catalyze ortho-ring fission to open the aromatic ring and continue metabolism. (b) CBA 3,4-(4,5)-dioxygenase pathway. The cbaABC genes encode dioxygenase, reductase, and dehydrogenase enzymes that initiate 3-CBA and 3,4-DCBA (not shown) degradation. Protocatechuic acid is also formed in this pathway. The host’s protocatechuate 4,5-dioxygenase (meta-ring-fission) enzymes then complete the pathway. (c) 4-CBA dehalogenase pathway. The fcbA gene encodes a 4-CBA-CoA ligase; fcbB encodes the dehalogenase; fcbC encodes a 4-hydroxybenzoate-CoA thioesterase. Note that the gene order in the control strain Pseudomonas sp. strain CBS-3 is fcbBAC.