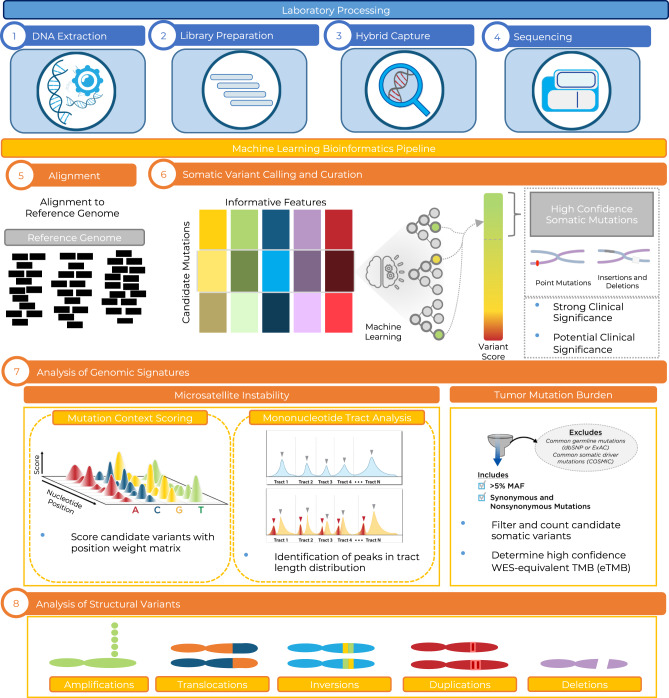
Fig. 1. Overview of sample preparation and analysis for determination of sequence and structural alterations, TMB, and MSI by elio tissue complete.
Genomic libraries were prepared using DNA extracted from cell line or FFPE tissue, and following hybrid capture and PCR amplification, DNA libraries were sequenced using the Illumina NextSeq. Next-generation sequencing data were analyzed using the VariantDx bioinformatics pipeline through alignment to the human reference genome assembly for the identification of sequence mutations, including single base substitutions (SBSs) and insertions/deletions (indels). Candidate variants were filtered through the PGDx Cerebro algorithm, designed to distinguish genuine somatic mutation calls from technical artifacts23 and used to determine an elio-predicted exome tumor mutation burden (eTMB) score. Microsatellite status was determined using 68 mononucleotide tracts and specific sequence mutation contexts. Structural variants were identified with the Digital Karyotyping (DK)29 and Personalized Analysis of Rearranged Ends (PARE)29 algorithms. TMB tumor mutation burden, MSI microsatellite instability, MAF mutant allele fraction, WES whole-exome sequencing.