Figure 1.
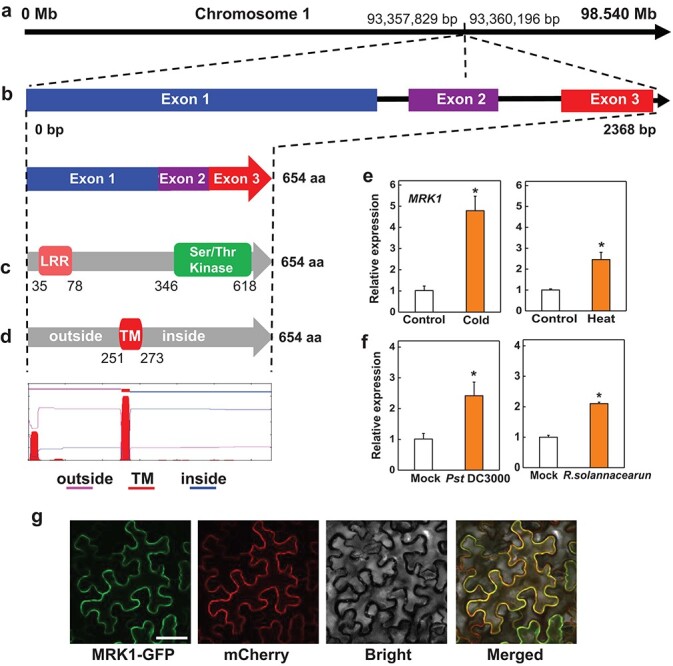
Bioinformatics and expression characteristics of tomato Multiple resistance-associated kinase 1 (MRK1). a, b The chromosomal locus and exon-intron structure of MRK1. Data were retrieved from the Solanaceae Genomics Network. c The functional domains of MRK1 determined using Pfam. d Illustration of the putative transmembrane region of MRK1 predicted by TMHMM V2.0. The expression profiles of MRK1 in response to cold (4°C) and heat (45°C) stress (e) and Pst DC3000 and R. solanacearum inoculation (f) were quantified using qRT-PCR with ACTIN2 as a normalization control. Samples were collected at 6 hours after exposure to cold or heat stress, at 12 hours after Pst DC3000 infection, and at 3 days after R. solanacearum inoculation. h Subcellular localization of MRK1. The tomato MRK1-GFP plasmid was transiently expressed in N. benthamiana leaves. The GFP and mCherry (a plasma membrane marker) signals were visualized by confocal microscopy at 48 h after infiltration. Bars = 50 μm. An asterisk indicates a significant difference between treatments (P < 0.05, Tukey’s test). The results in e and f are presented as mean values ± SD; n = 3. The experiment was performed three times with similar results.
