Figure 7.
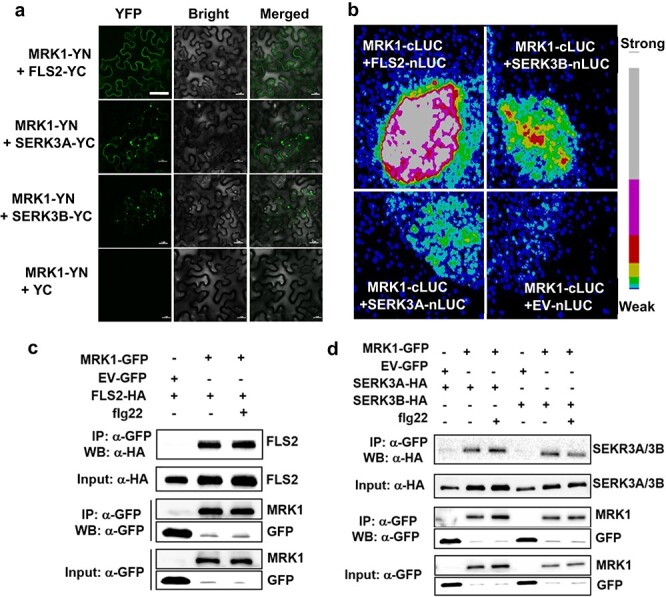
MRK1 associates with FLS2 and SERK3A/SERK3B in a complex. a Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays showing MRK1 interaction with FLS2 and SERK3A/SERK3B. MRK1-YFPN and FLS2-YFPC or SERK3A/SERK3B-YFPC were co-transfected into N. benthamiana leaves. The YFP fluorescence was visualized under a confocal microscope at 2 d after transfection. At least two independent experiments were performed with similar results. Bars = 50 μm. b Split-luciferase (LUC) assays showing the interactions of MRK1 with FLS2 and SERK3A/SERK3B. MRK1-nLUC and FLS2-cLUC or SERK3A/SERK3B-cLUC were co-transfected into N. benthamiana leaves. The signal was visualized using a Photek camera. The pseudocolor bar indicates the range of luminescence intensity. These experiments were repeated three times with similar results. c, d Co-immunoprecipitation of MRK1 with FLS2 or SERK3A/SERK3B proteins in N. benthamiana. Proteins were extracted from N. benthamiana leaves expressing MRK1-GFP in combination with FLS2-HA (c) or SERK3A/SERK3B-HA (d) and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with GFP-trap beads followed by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibody. EV-GFP was used as a negative control. These experiments were performed twice with similar results.
