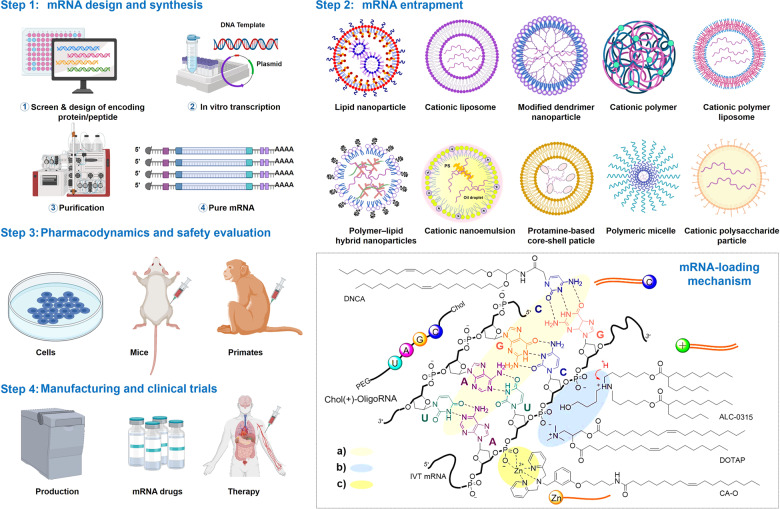
Fig. 2.
mRNA drugs production pipeline. The encoding of peptide/protein is designed and inserted into a plasmid DNA construct. Plasmid DNA is transcribed into mRNA by bacteriophage polymerases in vitro, and mRNA transcripts are purified by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or nanoprecipitation to remove contaminants and reactants. Subsequently, purified mRNA is entrapped in various vehicles. The interactions between vehicles and mRNA can be divided into three types: (a) electrostatic adsorption with phosphate ions of the ribonucleotides; (b) complementary paired hydrogen bonding with bases of the ribonucleotides; and (c) coordination with the phosphate ions. Thus, vehicles for mRNA delivery consist of the following categories: cationic compounds, such as cationic lipids, ionizable lipids, and cationic polymers. Nucleoside-based lipids, e.g., DNCA, or nucleoside-based amphiphilic polymers, e.g., Chol(+)-oligoRNA. Metal-based compounds provide vacant orbitals to coordinate with phosphate ions. Furthermore, the efficacy, pharmacology, and safety of mRNA drugs were evaluated in vaccinated mice and primates. Finally, the scale-up manufacturing of mRNA therapeutics is conducted and followed by clinical trials262