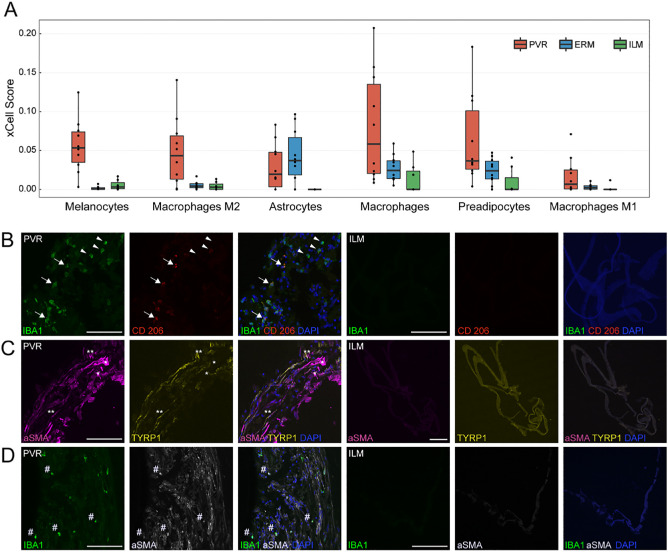
Figure 4.
Cellular composition of PVR, ERM, and ILM samples. (A) Cell type enrichment analysis of the sequencing data via xCell: six cell types were significantly enriched in PVR when compared to ILM tissue A. (B, C, D) Immunofluorescence staining of PVR (n = 5) and ILM (n = 5) specimens confirming the presence of IBA1-positive macrophages and CD206-positive M2 macrophages in PVR membranes, which are absent in ILM control specimens. Some of the IBA1-positive macrophages (arrows) co-expressed CD206 (arrow heads) suggesting a M2 polarization B. TYRP1-expression (melanocytes/RPE cells) was observed in one out of five PVR membranes and colocalized with α-SMA (double asterisks) pointing toward an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transdifferentiation of RPE cells to myofibroblasts. A subset of the α-SMA-positive cells, however, were negative for TYRP1 (single asterisk) pointing toward alternative cellular origins of myofibroblasts in PVR C. All five PVR membranes revealed IBA1-positive myeloid cells, such as hyalocytes, microglia, or macrophages, which co-expressed α-SMA (hashtag) suggesting a transdifferentiation of myeloid cells to myofibroblasts as a common pathophysiological feature during PVR formation D. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI. Scale bars correspond to 100 µm.