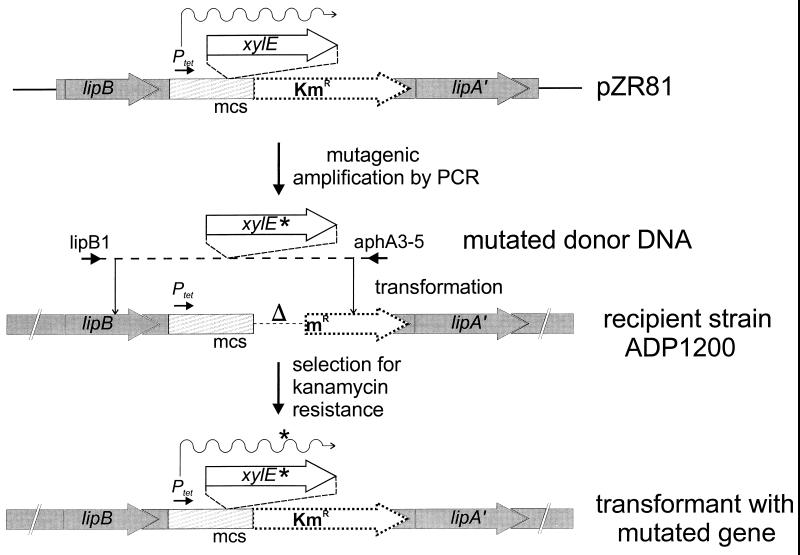
FIG. 1.
Random PCR mutagenesis of a heterologous gene (exemplified by P. putida xylE) and recovery of mutated genes for expression from a targeted site in the Acinetobacter chromosome. The plasmid pZR81 was prepared by the insertion of xylE into the multiple cloning site (mcs) of expression vector pZR80, downstream from the constitutive tet promoter (Ptet), and flanked by sequences homologous to the chromosome of recipient strain ADP1200. Strain ADP1200 lacks a functional aphA3 gene encoding kanamycin resistance. PCR was used to amplify xylE together with portions of lipB and aphA3, the latter encoding resistance to kanamycin. PCR DNA that may carry a PCR-generated mutation (∗) was used to transform ADP1200 to kanamycin resistance. A significant fraction of the kanamycin-resistant recombinants contained a mutant allele of the P. putida xylE docked into the chromosome of ADP1200. Thus, the procedure provides a way to produce and express single-copy mutant alleles of genes that lack a selectable mutant phenotype.