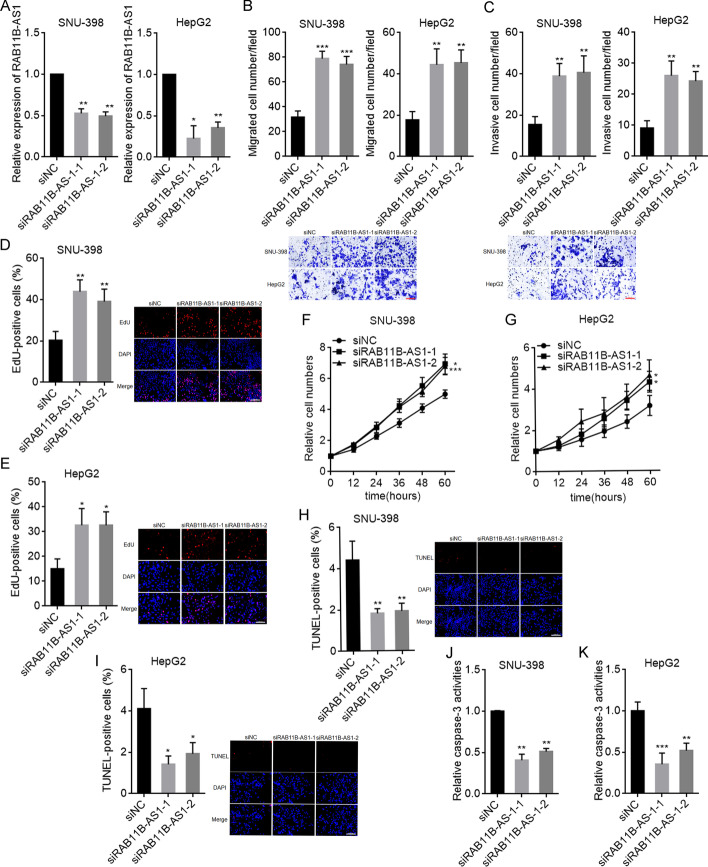
Fig. 7.
The roles of RAB11B-AS1 knockdown in HCC. A RAB11B-AS1 expression in SNU-398 and HepG2 cells with RAB11B-AS1 knockdown or control was detected by RT-qPCR. B Migration ability of SNU-398 and HepG2 cells with RAB11B-AS1 knockdown or control was detected by transwell migration assay. Scale bars, 100 µm. C Invasion ability of SNU-398 and HepG2 cells with RAB11B-AS1 knockdown or control was detected by transwell invasion assay. Scale bars, 100 µm. D Cellular proliferation of SNU-398 cells with RAB11B-AS1 knockdown or control was detected by EdU assay. Scale bars, 100 µm. E Cellular proliferation of HepG2 cells with RAB11B-AS1 knockdown or control was detected by EdU assay. Scale bars, 100 µm. F Cellular proliferation of SNU-398 cells with RAB11B-AS1 knockdown or control was detected by CCK-8 assay. G Cellular proliferation of HepG2 cells with RAB11B-AS1 knockdown or control was detected by CCK-8 assay. H Cellular apoptosis of SNU-398 cells with RAB11B-AS1 knockdown or control was detected by TUNEL assay. Scale bars, 100 µm. I Cellular apoptosis of HepG2 cells with RAB11B-AS1 knockdown or control was detected by TUNEL assay. Scale bars, 100 µm. J Cellular apoptosis of SNU-398 cells with RAB11B-AS1 knockdown or control was detected by caspase-3 activity assay. K Cellular apoptosis of HepG2 cells with RAB11B-AS1 knockdown or control was detected by caspase-3 activity assay. Results are shown as mean ± SD of n = 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test