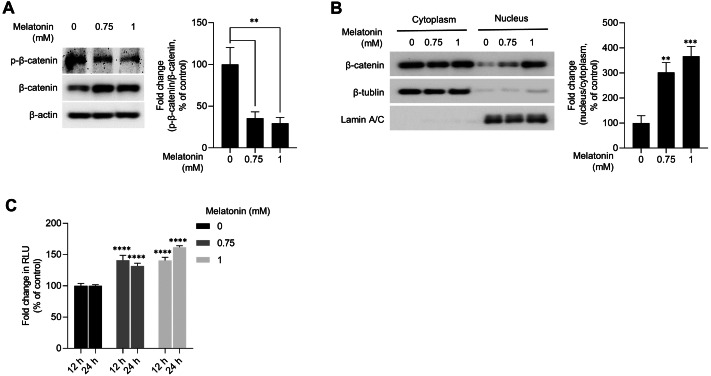
Figure 4. Effect of melatonin on β-catenin signaling pathway in HDP spheroids.
(A and B) HDP cells were treated with 0.75 and 1 mM melatonin for 24 h. (A) β-catenin stabilization was assessed by western blotting and β-actin served as a loading control. Quantification of the phosphorylation level was carried out using ImageJ software. (B) β-catenin translocation was assessed by western blotting. β-actin, Lamin C, and β-tubulin served as loading controls for total protein, nuclear fraction, and cytoplasmic fraction, respectively. Quantification of the phosphorylation level was carried out using ImageJ. (C) 293T cells were treated with 0.75 and 1 mM melatonin for 12 h and 24 h. TCF/LEF transcriptional activity was determined using a luciferase assay and normalizing luciferase activity to β-galactosidase activity. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (A and B) One-way ANOVA, followed by Turkey’s post hoc test; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 versus DMSO treated control (A, p = 0.0023, and p = 0.0014; B, p = 0.0012, and p = 0.0003 respectively). (C) Two-way ANOVA, followed by Turkey’s post hoc test; **** p < 0.0001 versus DMSO treated control (12 h, p < 0.0001, and p < 0.0001; and 24 h, p < 0.0001, and p < 0.0001 respectively).