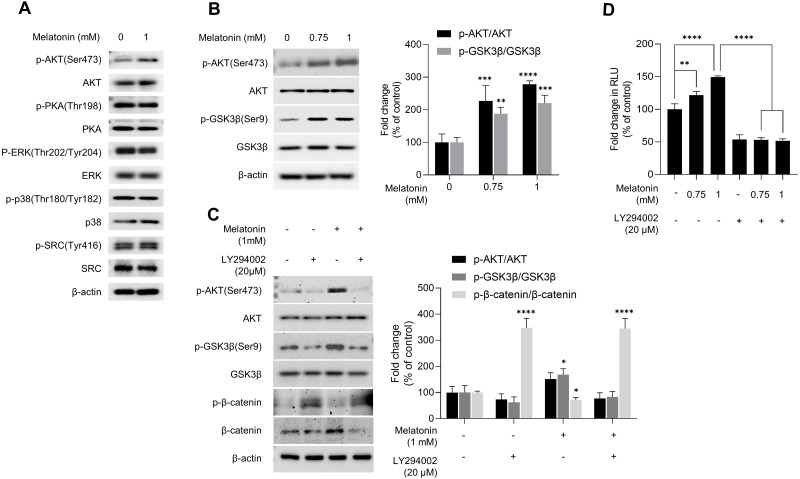
Figure 5. Effect of melatonin on AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling in HDP spheroids.
(A) HDP cells were treated with 1 mM melatonin for 24 h. Protein levels of GSK3 β upstream signaling target genes were assessed by western blotting and β-actin served as a loading control. (B) HDP cells were treated with 0.75 and 1 mM melatonin for 24 h. The level of AKT/GSK3 β signaling phosphorylation were assessed by western blotting. β-actin served as a loading control. (C) HDP cells were treated with 1 mM melatonin with or without 20 µM LY294002 for 24 h. Phosphorylation of AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling were assessed by western blotting and β-actin served as a loading control. Quantification of phosphorylated level was carried out using the ImageJ software. (D) 293T cells were treated with 1 mM melatonin with or without 20 µM LY294002 for 24 h. TCF/LEF transcriptional activity was determined using a luciferase assay by normalizing luciferase activity to β-galactosidase activity. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (B and C) Two-way ANOVA, followed by Turkey’s post hoc test; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 versus DMSO treated control (B: p-AKT/AKT, p = 0.0002, and p < 0.0001, and p-GSK3 β/GSK3β, p = 0.0041, and p = 0.0003; and C: p-GSK3 β/GSK3β; p = 0.0103, and p- β-catenin/β-catenin, p < 0.0001, and p < 0.0001 respectively). (D) One-way ANOVA, followed by Turkey’s post hoc test; ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001 versus DMSO treated control (p = 0.004, and p < 0.0001 respectively) and, versus LY294002 untreated control (p < 0.0001, and p < 0.0001 respectively).