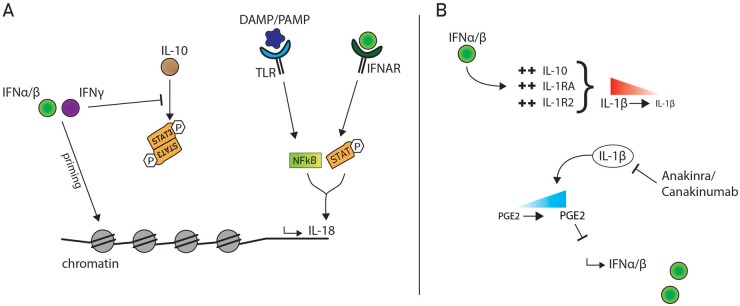
Fig. 2.
IFN crosstalk and signalling pathway modulation
(A) Type I and II IFNs modulate the immune response by epigenomic changes. IFN-γ inhibits the anti-inflammatory response of IL-10 by interfering with STAT3 signalling. IFNα/β signalling via IFNAR and DAMPs/PAMPs signalling via TLRs can work together to induce transcriptional regulation of IL-18. (B) IFNα/β downregulates IL-1α/β by upregulation of IL-10, IL1RA and the decoy IL-1R2 receptor. IL-1 suppresses IFNα/β production via Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) upregulation. Anakinra/Canakinumab, which blocks IL-1 signalling, can thus promote increased IFNα/β levels.