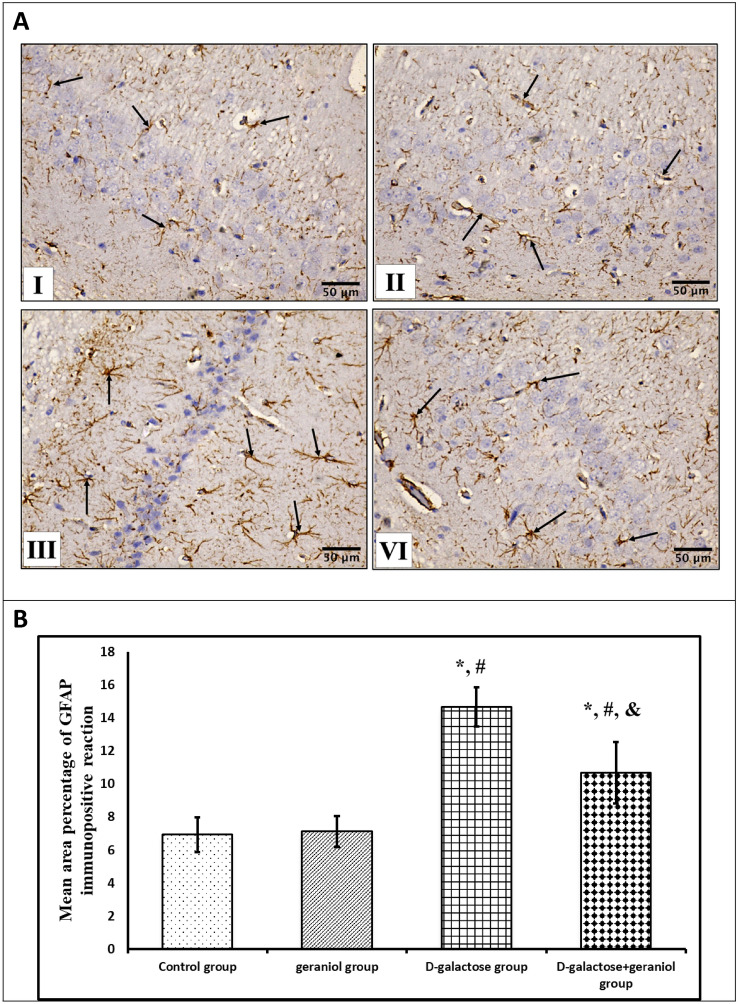
Fig. 5.
A Effect of geraniol treatment on hippocampal glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunoreactivity (arrows) in all the studied groups; Control and geraniol groups (I & II) exhibit apparent few GFAP-positive reactive cells in CA1 area, d-galactose group (III) shows an apparent increased number of GFAP-positive reactive cells in CA1 area, and d-galactose + geraniol group (IV) shows an apparent decreased number of GFAP-positive reactive cells in CA1 area (GFAP X 400, scale bar = 50 μm). B Effect of geraniol treatment on the mean area percentage of GFAP immunopositivity reaction. Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. (n = 10/group). Statistical analysis was carried out using one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test, SPSS computer program. *Mean significant difference vs control group (P < 0.05) #Mean significant difference vs geraniol group (P < 0.05). &Mean significant difference vs d-galactose group (P < 0.05)