FIGURE 1.
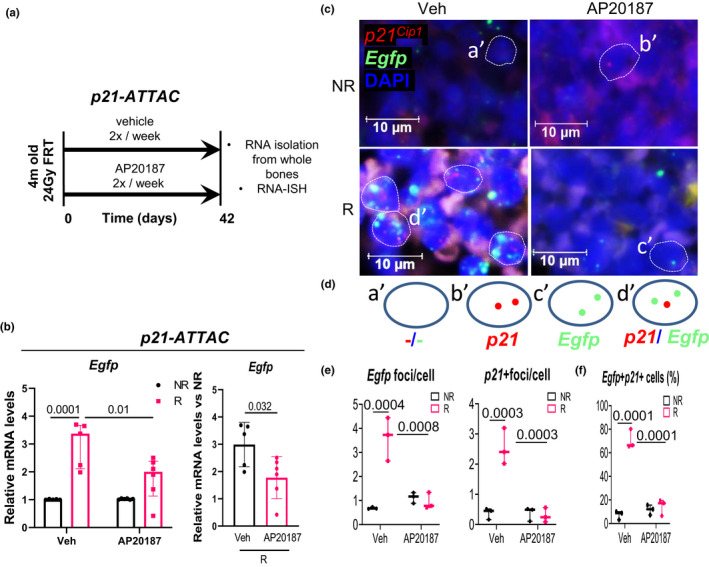
Validation of the p21‐ATTAC mouse model using radiation as an inducer of senescence. (a) Schematic showing the experimental design for the p21‐ATTAC mice. The right legs of the mice were radiated (24 Gy) near the femoral metaphysis (5 mm above the growth plate), while the left leg served as control. Starting from day 1 post radiation, the animals received vehicle or AP20187 for 2 times per week for 6 weeks. Radiated (R) and nonradiated (NR) femurs at 42 days post‐radiation were collected for qRT‐PCR. (b) The Egfp transgene was activated in R bones, and the expression levels were significantly reduced in the AP20187‐treated animals. Statistical comparisons between the groups (left panel in b) was done by an ordinary two‐way ANOVA, with a Tukey’s post‐hoc analysis. (Right panel in b) The Egfp expression was normalized to the NR control leg for each animal. Statistical comparison was done using a two‐tailed unpaired t test between the Veh‐R and AP20187‐R bones. (c) RNA‐in situ hybridization (RNA‐ISH) was performed using probes against p21 Cip1 (shown in red) and Egfp (shown in green) transcripts. (d) Four populations of bone marrow cells, one with DAPI alone (a′), second expressing p21 Cip1 (b′), a third expressing Egfp (c′), and a fourth expressing both p21 Cip1 and Egfp (d′) were used to generate two kinds of data, one quantifying Egfp and p21 Cip1 foci per cell as shown in (e), and second quantifying percentage of bone marrow cells that expressed p21 Cip1 and Egfp, Egfp alone and p21 Cip1 alone (f). Statistical comparisons were calculated using an ordinary two‐way ANOVA, with a Tukey’s post‐hoc analysis
