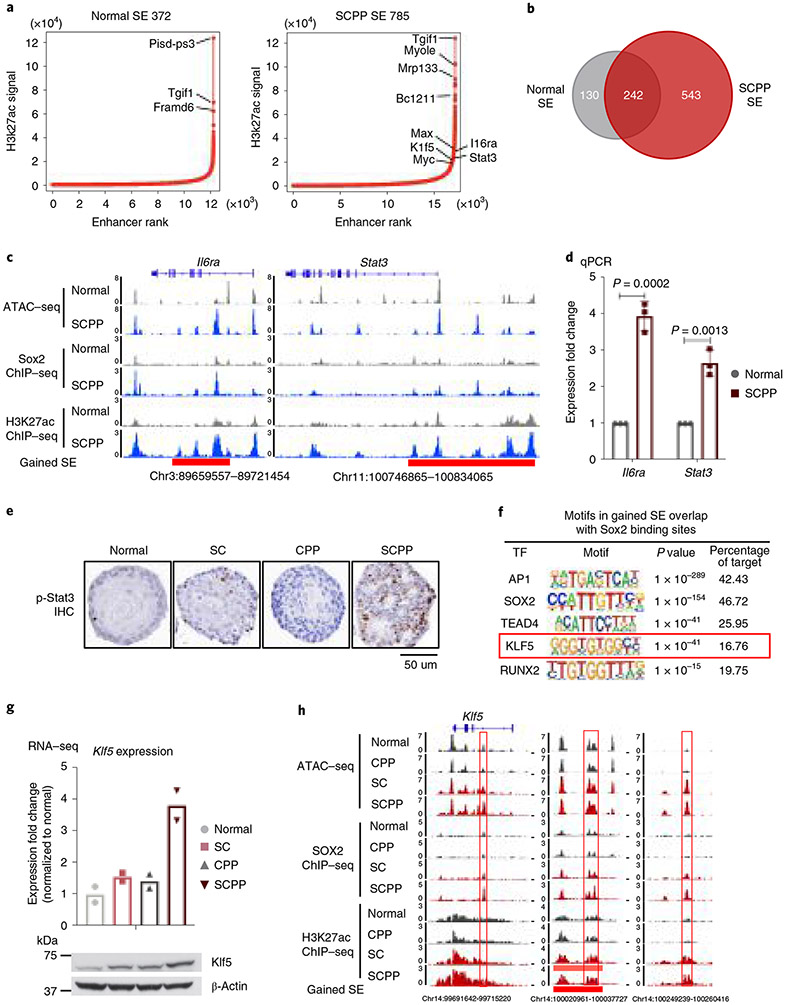
Fig. 3 ∣. Sox2 overexpression is associated with new SEs and Klf5 activation.
a, ‘Hockey-stick’ plots show putative enhancers and SEs determined by H3K27ac ChIP–seq in normal and SCPP organoids. The horizontal line represents the demarcation between typical enhancers (below) and SEs (above). b, Venn diagram shows overlap of SEs identified in normal and SCPP organoids. c, Representative ATAC–seq, Sox2 ChIP–seq and H3K27ac ChIP–seq tracks, showing increased chromatin accessibility, gained Sox2 binding, increased H3K27ac level and formation of de novo SEs at the Stat3 and Il6ra loci in SCPP versus normal organoids. d, mRNA expression of Stat3 and Il6ra in SCPP and normal organoids as measured by RT–qPCR. Data are shown as mean±s.d. Three independent biological replicates were performed for each organoid. P values calculated by two-sided unpaired t-test. e, Representative IHC staining of phospho-Stat3 level in different organoids. (This experiment was repeated once with similar results.) f, Top transcription factor motifs enriched in de novo SEs bound by Sox2 in SCPP organoid; P values were calculated by the HOMER package. g, mRNA expression (RNA-seq) and immunoblot of Klf5 in different organoids. Two biological replicates were performed for each organoid. h, Representative ATAC–seq, Sox2 ChIP–seq and H3K27ac ChIP–seq tracks show increased chromatin accessibility, gained Sox2 binding, increased H3K27ac level and formation of de novo SEs at the Klf5 locus in Sox2-overexpressed organoid. Selected peaks are highlighted in red boxes.