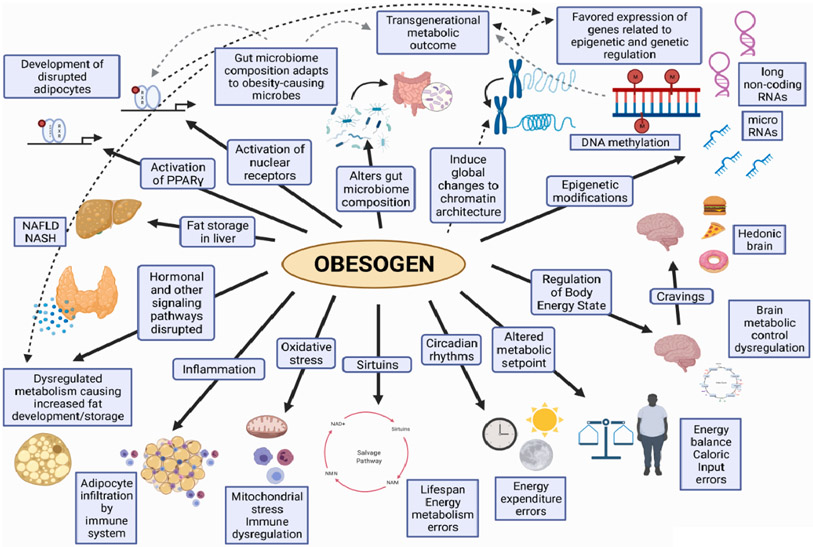
Fig. 6. Composite of sites and mechanisms of obesogens.
Obesogens, as described in the text, can act via a variety of mechanisms and act on a variety of tissues. Some mechanisms are direct, such as receptor mechanisms and epigenetic changes and some, such as sirtuins, oxidative stress, inflammation, circadian rhythms, alterations in food intake and food addiction, and increase in number and size of fat cells, can result from the initial mechanisms. Obesogens have both direct and indirect actions on several tissues like liver, pancreas, muscle, gut microbiome, and brain. Thus, obesogens can disrupt all the sites and tissues known to be involved in control of metabolism.