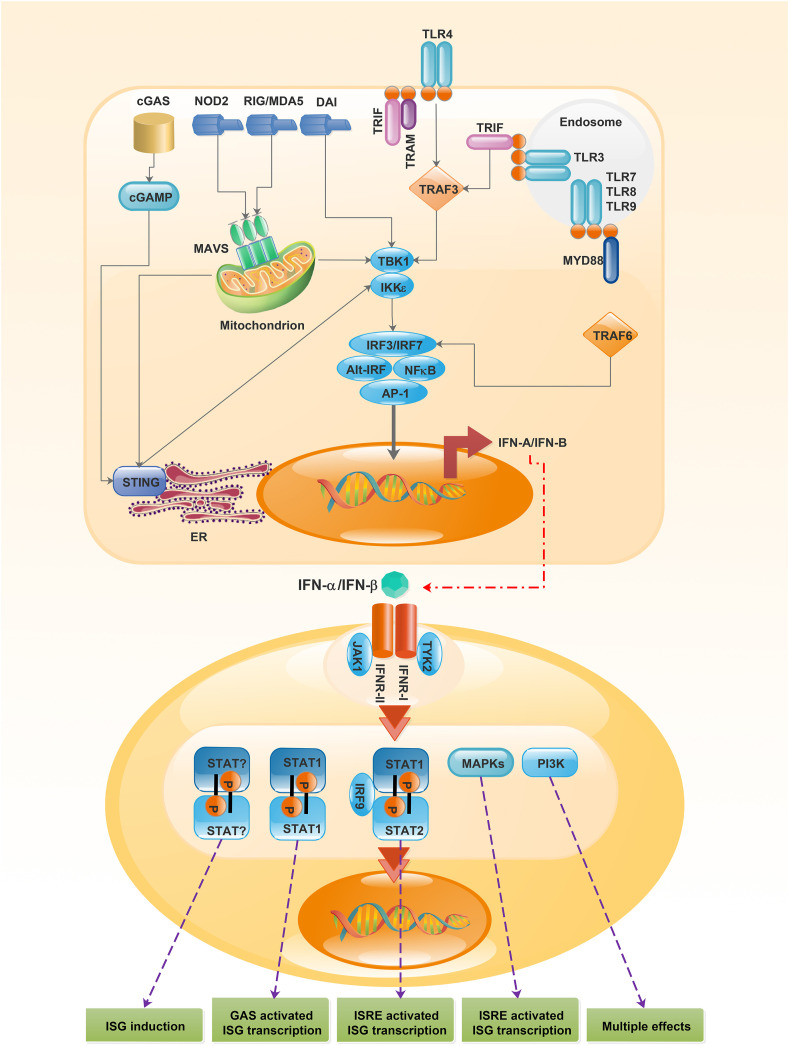
Fig. 1.
Interferon α/β production and receptor signaling. Recognition of microbial products by a range of PRR on the surface or inside the cell activates several distinct signaling pathways, inducing the expression of the genes encoding IFN α/β. Attachment of IFN-Is to IFN-α receptor stimulates several signaling pathways, creating different biological effects in the cell. The classical pathway contains STAT1–STAT2–IFN-IRF9 signaling complex (also known as ISGF3 complex). This complex binds to ISREs in gene promoters and activates ISGs. Heterodimers and homodimers of some STAT molecules including STAT3, STAT4, and STAT5 may also be activated downstream. MAPKs and the PI3K pathways are STAT independent signaling pathways that can also be involved following recognition of IFN α/β by the receptor. PRR, pattern recognition receptors; IFN α/β, Interferon α/β; IFN-I, type-I interferon; IFNAR, IFN-α receptor; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; IRF9, IFN-regulatory factor 9; ISGF3, IFN-stimulated gene factor 3; ISREs, IFN-stimulated response elements; ISGs, IFN-stimulated genes; MAPKs, mitogen-activated protein kinases; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3 kinase; cGAS, cytosolic GAMP synthase; NOD2, NOD-containing protein 2; RIG, retinoic acid-inducible gene; MDA5, melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5; DAI, DNA-dependent activator of IRFs; TLR, toll like receptor; TRIF, TIR domain-containing adaptor protein inducing IFNβ; TRAM, TLR adaptor molecule (also known as TICAM2); TRAF, TNF receptor-associated factor; cGAMP, cyclic di-GMP-AMP; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein; TBK1, TANK-binding kinase 1; IKKε, IκB kinase-ε; MYD88, myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88; IRF, IFN-regulatory factor; Alt-IRF, IRFs other than IRF3 or IRF7; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; AP-1, activator protein 1; STING, stimulator of IFN genes; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; TYK2, tyrosine kinase 2; JAK1, Janus Kinase 1; GAS, γ-activated sequence.