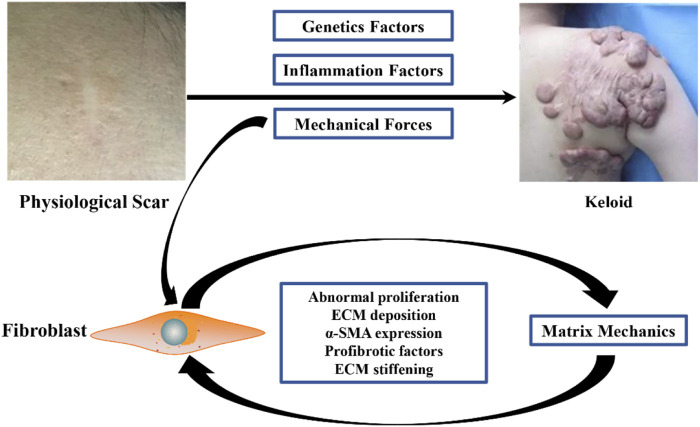
FIGURE 1.
Causes of keloid matrix stiffening during fibrotic progression. Mechanical stimulation can lead to excessive proliferation of wound fibroblasts, deposition of ECM, secretion of more pro-fibrosis factors, and continuous increase of matrix stiffness of keloid ECM. Matrix mechanics resulting from elevated matrix stiffness further activates the fibrotic phenotype of keloid fibroblasts, thus forming a loop that continuously invades surrounding normal tissue.