FIGURE 1.
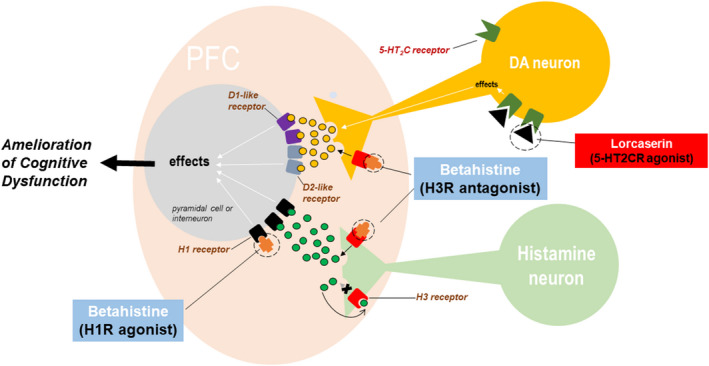
Hypothesis: Lorcaserin plus betahistine synergistically enhances mesocortical dopamine and ameliorates cognitive dysfunction in obese animals. Both lorcaserin and betahistine increase dopamine release in the PFC, but they produce the effect via different mechanisms. Lorcaserine activates serotonine 5‐HT2C receptors on mesocortical dopaminergic neurons to increase their firing rate. Betahistine blocks the inhibitory histamine H3 receptors on dopaminergic neurons. When co‐administered, the two drugs would act synergistically to restore the mesocortical dopamine deficit in obese animals and ameliorate cognitive dysfunction caused by the reduced activation of both D1‐ and D2‐like receptors on PFC pyramidal cells and interneurons. Betahistine may exert additional pro‐cognitive effects by stimulating H1 receptors and increasing the release of histamine and other transmitters such as acetylcholine and norepinephrine in the PFC 25
