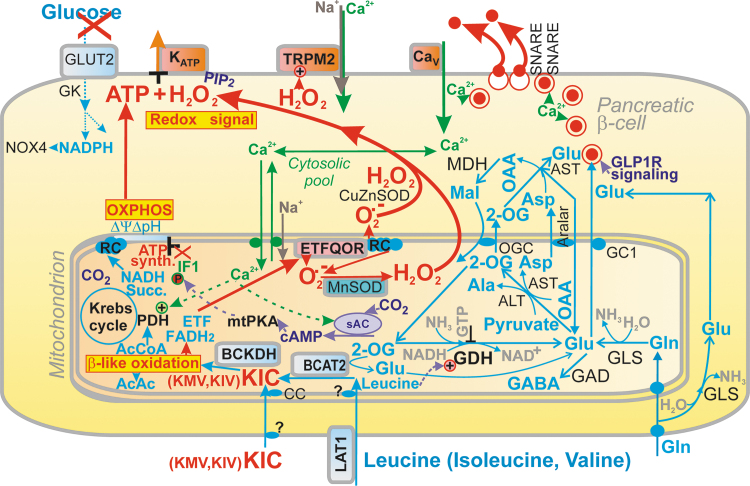
FIG. 9.
Mitochondrial retrograde redox signaling determines insulin secretion by BCKAs. KIC, KMV, and KIV may arise from blood capillaries (imported into the matrix via the carnitine carrier, CC) or by being converted from leucine, isoleucine, and valine, respectively, by the branched-chain aminotransferase reaction in the mitochondrial matrix (BCAT2). The BCAA import is ensured by the plasma membrane LAT1 transporter. The BCKDH, which provides electrons to ETF, exists exclusively in β-cell mitochondria and initiates a series of reactions of β-like oxidation. ETF:QOR accepts electrons from two ETFs, when it converts Q to QH2, and as side reactions produces superoxide together with its elevated production at sites IQ and IIIQo (cf. Fig. 11). In the mitochondrial matrix, superoxide is transformed to H2O2 by MnSOD, but by CuZnSOD in the intermembrane space and cytosol. The elevated mitochondrial/cytosolic H2O2 substantiates the retrograde redox signaling that targets KATP to ensure its closure together with ATP (and possibly also TRPM2). As a result, CaV channels are open, providing the Ca2+-signal for IGV exocytosis. The end products of the β-like oxidation of KIC contribute to OXPHOS. Thus, AcCoA enters the Krebs cycle to form citrate, whereas AcAc can be partly exported to the cytosol or converted to β-OHB by a reverse reaction of β-OHBDH at the expense of NADH (Fig. 8). A link to glutamate and glutamine metabolism is also indicated, including the MAS (Fig. 7), which may exist together with BCKA-stimulated insulin secretion at low glucose, since at low glucose, the pyruvate-based redox shuttles are not highly active. AcAc, acetoacetate; AcCoA, acetyl-CoA; BCAA, branched-chain amino acid; BCAT2, branched/chain amino acid transferase 2, mitochondrial; BCKA, branched-chain ketoacid; BCKDH, branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase; ETF, electron transfer flavoprotein; ETFQOR or ETF:QOR, electron transfer flavoprotein:quinone oxidoreductase; GAD, glutamate decarboxylase; GC1, glutamate carrier; GLS, glutaminase; IGV, insulin granule vesicle; KIC, 2-ketoisocaproate; KIV, 2-ketoisovalerate; KMV, 2-ketoisomethylvalerate; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; Q, ubiquinone; QH2, ubiquinol.