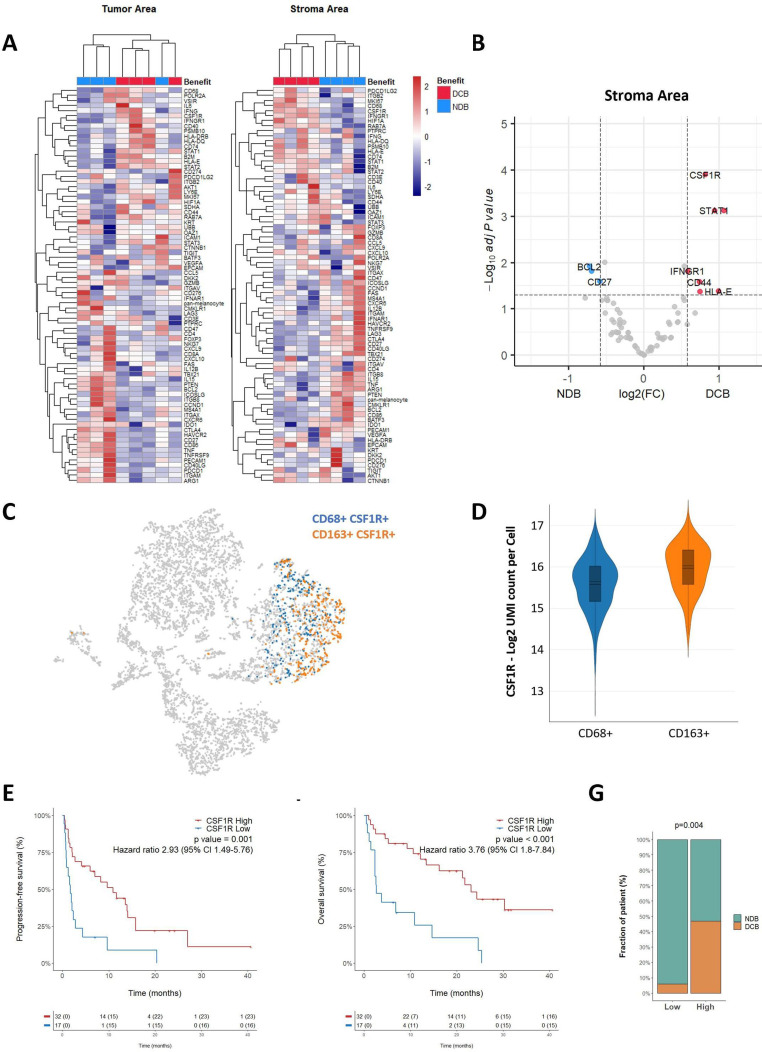
Figure 3.
M1-associated genes are enriched in immunotherapy-responsive patients with high level of CD163+ cell infiltration. (A) Unsupervised clustering of patient with tumor samples based on the averaged expression of the GeoMX Immune Pathways Panel probes in the tumor and stroma areas. The patient response classified as non-clinical benefit (NDB—blue) and durable clinical benefit (DCB—red) is annotated. (B) Volcano plot representation of the gene differentially expressed in the stroma areas of patients who experienced DCB and NCB. (C) tSNE visualization of 10× scRNA-seq of non-small cell lung cancer biopsy. Cells co-expressing CD68 or CD163 together with CSF1R are highlighted in blue and orange, respectively. (D) Representation of CSF1R expression in CD68+ and CD163+ cells, as assessed by scRNAseq. (E–F) Kaplan-Meier curves of progression-free survival (E) and overall survival (F) of patients according to the expression of CSF1R determined by RNAseq and classified as high or low. (G) Proportion of patients who experienced DCB or NCB according to their level of CSF1R expression determined by RNAseq and classified as high and low. P value was calculated using χ2 test. IFN, interferon; RNAseq, RNA sequencing; scRNA -seq, single cell RNAseq. tSNE, t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding.