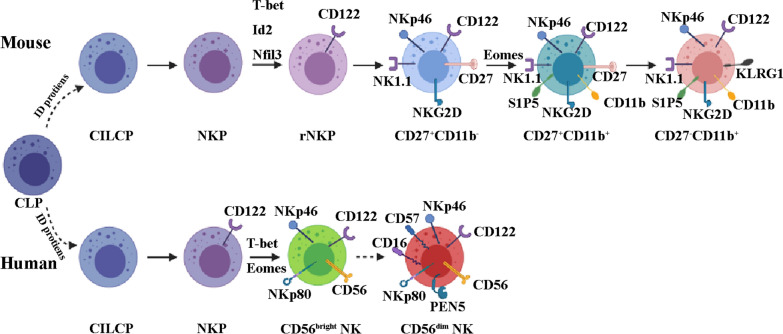
Fig. 2.
NK cell development. In mice, common lymphoid progenitor (CLP) produces common ILC precursor, CILCP). CILCP can produce NK cells and helper-like ILCs. There are at least five other stages in NK cell development from CILCP: NK progenitor cells (NKP), refined-NKP (rNKP), CD27+CD11b−NK, CD27+CD11b+NK and CD27−CD11b+ NK. In humans, after CILCP is developed from CLP, NK-restricted NKP will be developed from the latter. NKs is characterized by expressing CD122, losing CD34 and CD127. The expression of T-bet and Eomes is needed for further differentiation into functional NK cells. The expression of CD56 can divide NK cells into two subgroups: CD56dim and CD56bright. The two subsets express activated surface receptors NKp46 and NKp80. CD56+ NK cells can differentiate into CD56− NK cells by expressing CD16, PEN5 and CD57