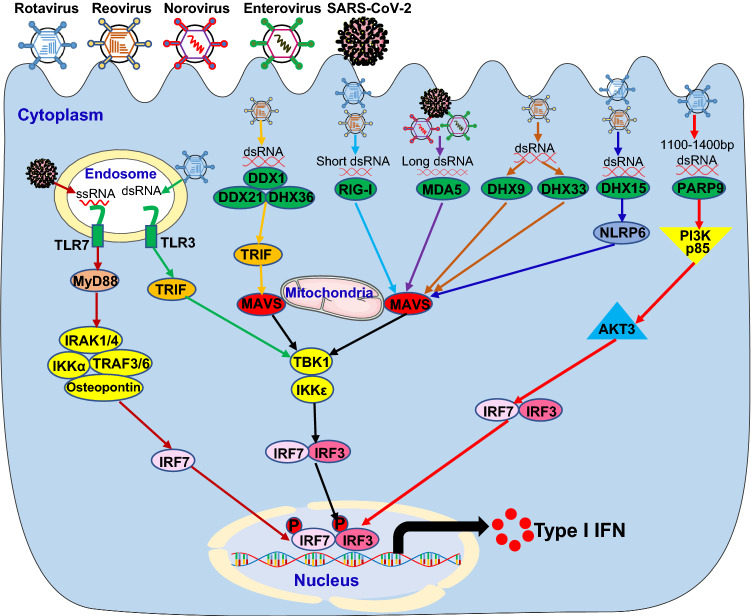
Fig. 2.
Host PRRs sense enteric RNA viruses to induce type I IFN signaling pathway. Invasion by enteric RNA viruses, including rotavirus, reovirus, norovirus, enterovirus and SARS-CoV-2, introduces RNA into the endosome or dsRNA in the cytoplasm. The host pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), including TLR3 and TLR7 in the endosome and DDX1/DDX21/DHX36 complex, RIG-I, MDA5, DHX9, DHX33, DHX15 and PARP9 in the cytoplasm, recognize the RNA molecules and trigger the activation of downstream cascades through their adaptors leading to the induction of type I IFN in innate immune cells of the intestinal tract. MyD88 Myeloid differentiation primary response 88, TRIF TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β, IRAK1/4 Interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase 1 and 4, IKKα IκB kinase α, TRAF3/6 TNF receptor-associated factor 3 and 6, IRF7 Interferon regulatory factor 7, DDX1 DEAD-Box helicase 1, RIG-I Retinoic acid-inducible gene I, MDA5 Melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5, DHX15 DEAH-Box helicase 15, PARP9 Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 9, MAVS Mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein, TBK1 TANK-binding kinase 1, NLRP6 the NACHT, LRR, and PYD domains-containing protein 6, PI3K p85 Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) regulatory subunit p85, AKT3 AKT Serine/Threonine kinase 3