Fig. 4.
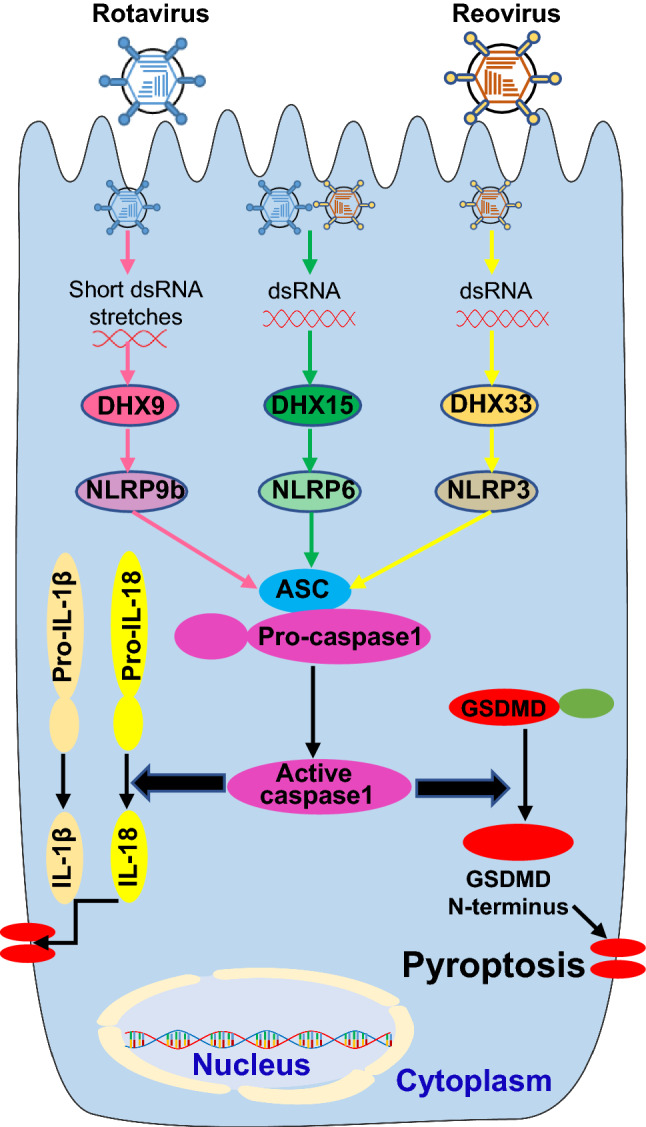
Host PRRs sense enteric RNA viruses to induce inflammasome activation signaling pathway. Entering by enteric RNA viruses, including rotavirus and reovirus, introduces dsRNA in the cytoplasm. The host PRRs in the cytoplasm, including DHX9, DHX15 and DHX33, recognize the RNA molecules and trigger the activation of inflammasome containing ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain), pro-caspase1 and NLRP9b (the NACHT, LRR, and PYD domains-containing protein 9b), NLRP6 or NLRP3, which results in cleavage of pro-caspase1 into active caspase1. The active caspase 1 mediates maturation and secretion of IL-18 and IL-1β cytokines by cleavage of pro-IL-18 and pro-IL-1β. Additionally, active caspase 1 can provoke a lytic form of cell death termed pyroptosis through cleavage of its substrate Gasdermin D (GSDMD) into GSDMD N-terminus that forms pores in the cellular membrane
