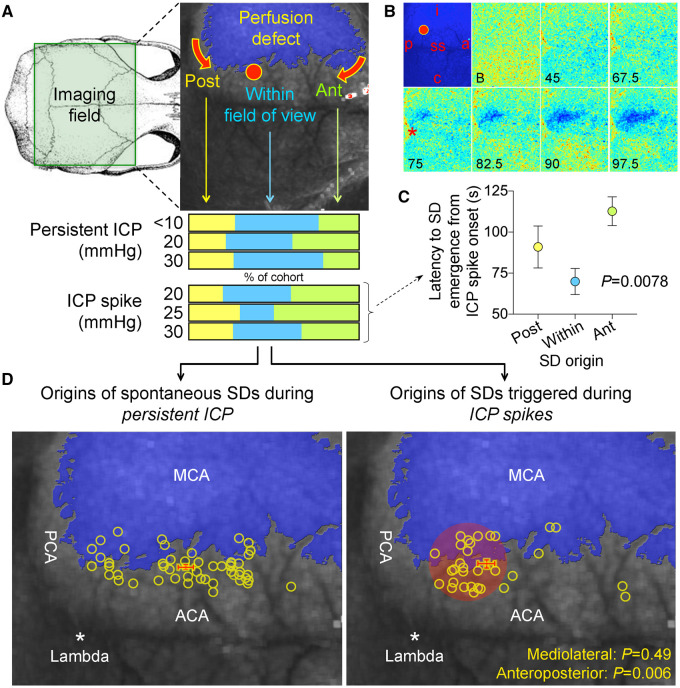
Figure 3.
Origins of SDs. (A) Full-field laser speckle imaging of CBF over the dorsal cortex shows the origins of SDs in relation to the perfusion defect (blue overlay). About 1/3 of SDs propagated into the imaging field from the anterior (Ant, green) and a third from the posterior (Post, yellow), while the remainder originated from the peri-infarct regions within the imaging field of view (blue). Horizontal bars below show the distribution of SD origins in persistent ICP and ICP spike groups at different ICP levels. The distribution did not statistically differ among ICP levels or between persistent or transient ICP elevation groups (χ2). (B) Time lapse laser speckle images of relative CBF changes (blue indicates a decrease, red indicates an increase in CBF from baseline image, B) show the origin of a typical SD within the field of view (red circle) and its propagation throughout the peri-infarct cortex in a representative experiment during a 30-s, 30 mmHg ICP spike. The top left image shows the position of the imaging field as in Fig. 5A (a = anterior; p = posterior; i = ipsilateral to fMCAO; c = contralateral; ss = sagittal sinus; red circle, SD origin). Time (in seconds) after ICP spike onset is indicated on the lower left of each frame (B, baseline). SD onset is visible at 75 s marked by a focal hypoperfusion developing near lambda (*), as marked on the upper left frame by a red circle. (C) The latency between ICP spike onset and SD emergence in the field of view differed among SDs originating within the field of view and propagating into the field anteriorly or posteriorly (P = 0.0078; one-way ANOVA). (D) Spatial distribution of the origins of SDs that started within the field of view during steady state ICP (left) and during 30-s, 30 mmHg ICP spikes (right), regardless of ICP level or spike duration. Each yellow circle indicates an SD. The centre of the red cross indicates the average mediolateral and anteroposterior coordinates of SDs in each group with standard errors in mediolateral (vertical error bar) and anteroposterior (horizontal error bar). All SDs originated from the peri-infarct tissue. The mediolateral coordinates of SD origins did not differ between persistent and transient ICP groups (P = 0.49). In contrast, SDs originating during an ICP spike were significantly more posterior compared with persistent ICP group (P = 0.006; Student’s t-test). Indeed, most spike-induced SDs originated from the watershed region among anterior, middle and posterior cerebral arteries (red shaded area). ACA = anterior cerebral artery; PCA = posterior cerebral artery.