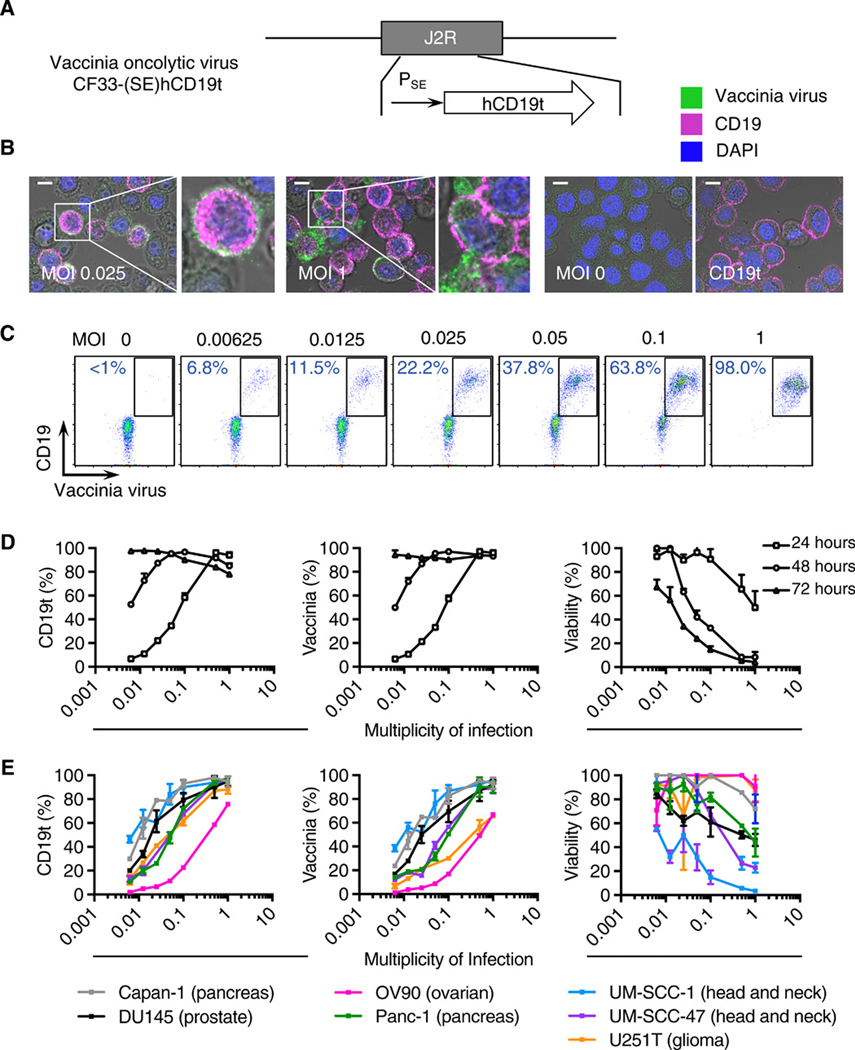
Fig. 1. OV effectively deliver CD19t to solid tumors in vitro.
(A) Schematic of vaccinia OV [CF33-(SE)hCD19t], showing incorporation of human truncated CD19 (CD19t) under the control of the synthetic early promoter (PSE) inserted into the J2R locus and replacing the thymidine kinase gene. (B) Immunofluorescence microscopy of MDA-MB-468 cells infected for 24 h with OV19t at multiplicity of infection (MOI) 0.025 or MOI 1, untransduced (MOI 0), or cells transduced with lentivirus to stably express CD19t. Scale bars, 10 μm. Blue is DAPI, pink indicates CD19t, and green indicates vaccinia. (C) FACS plots of MDA-MB-468 tumor cells positive for CD19t and vaccinia virus after 24 h of OV19t infection at increasing MOIs. Percents indicate CD19t-positive, virus-positive population in the boxed region. (D) Quantification of percent CD19t positive (left), vaccinia positive (middle), and viable (right) MDA-MB-468 tumor cells following 24, 48, and 72 h exposure to the indicated MOIs of OV19t. (E) Quantification of CD19t positive (left), vaccinia positive (middle), and viable (right) cells of indicated solid tumor cell lines following 24, 48, and 72 h exposure to the indicated MOIs of OV19t. Data in B and C are from one of at least two independent experiments. Data in D and E are presented as mean + SD (D) or mean ± SD (E) (n ≥ 2) from one of at least three independent experiments.